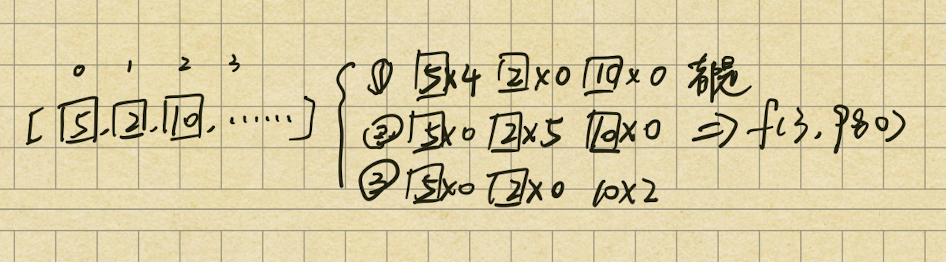高频题 三数之和 两数之和 为基础
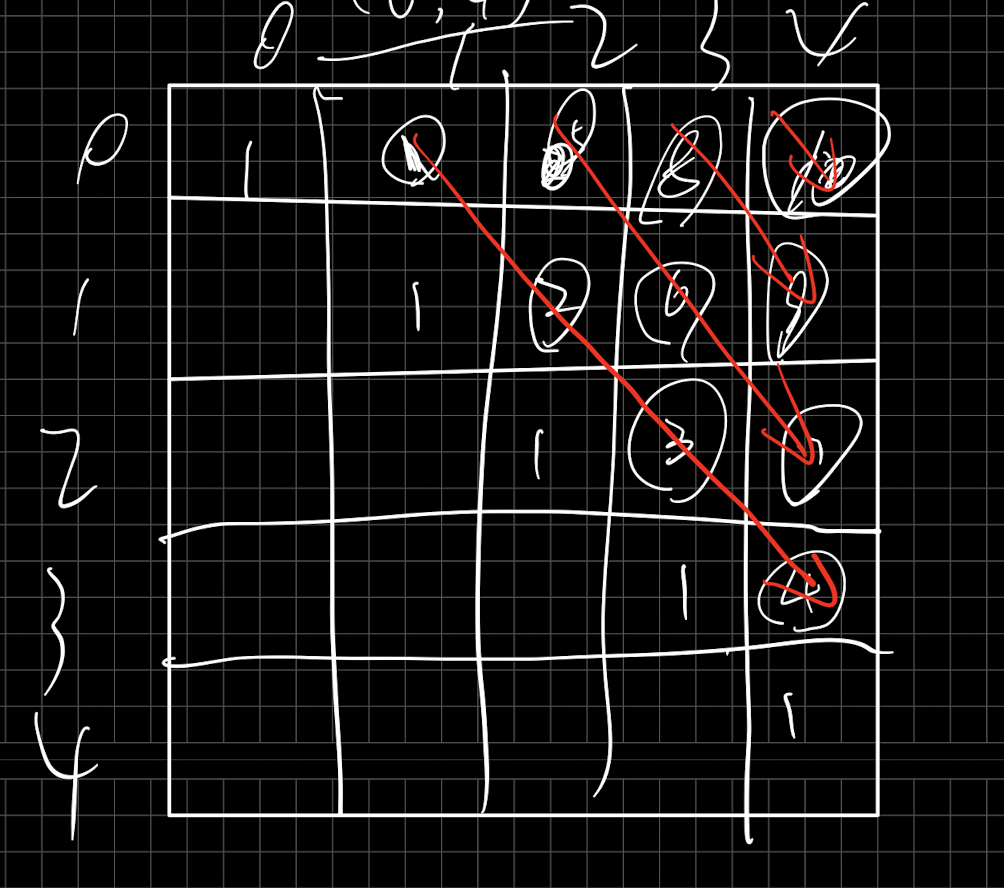
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); int N = nums.length; List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = N - 1 ; i > 1 ; i--) { if (i == N - 1 || nums[i] != nums[i + 1 ]) { List<List<Integer>> nexts = twoSum(nums, i - 1 , -nums[i]); for (List<Integer> cur : nexts) { cur.add(nums[i]); ans.add(cur); } } } return ans; } public static List<List<Integer>> twoSum (int [] nums, int end, int target) { int L = 0 ; int R = end; List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>(); while (L < R) { if (nums[L] + nums[R] > target) { R--; } else if (nums[L] + nums[R] < target) { L++; } else { if (L == 0 || nums[L - 1 ] != nums[L]) { List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList <>(); cur.add(nums[L]); cur.add(nums[R]); ans.add(cur); } L++; } } return ans; }
两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
1 使用hashmap 结构 map.put(nums[i], i)
2 遍历一遍 如果查询到map里面有与解 就返回i和mapget的value
3 最后如果没有找到就返回new int[0]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i ++){ if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])){ return new int []{i, map.get(target - nums[i])}; } map.put(nums[i], i); } return new int [0 ]; } }
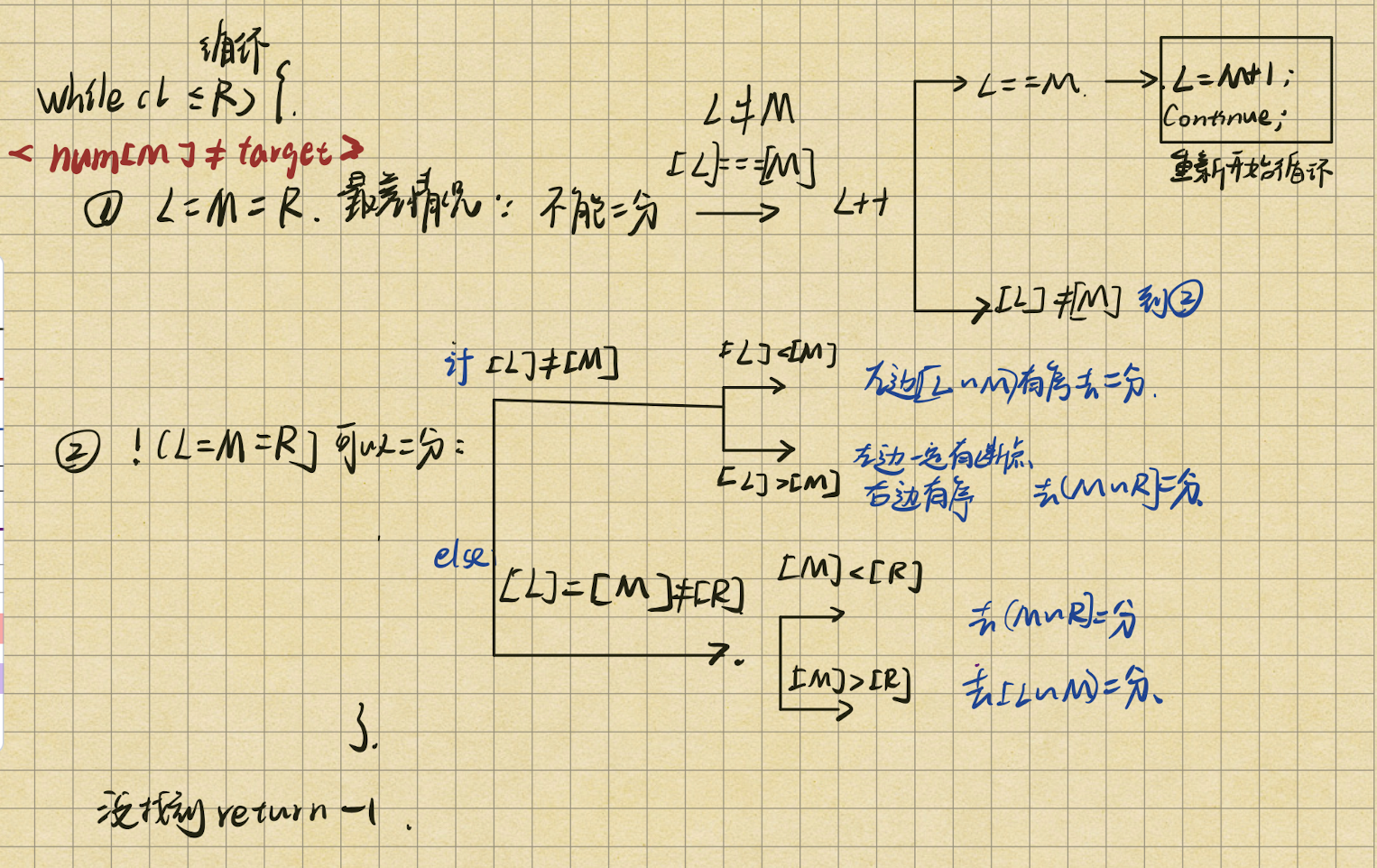
搜索旋转排序数组(面试) 使用二分查找
整数数组nums按升序排列,数组中的值互不相同。
arr,原本是有序数组,旋转过,而且左部分长度不知道.(以某一个下标为轴旋转 例如, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 在下标 3 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] 。)
题目需要在arr里面找到target
思路 :
L = M = R 是最差的情况 不知道断点L != M == R/ L == M != R/ L != M != R 只要三个数不全部一样就可以进行二分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public int search (int [] nums, int target) { int N = nums.length; int L = 0 ; int R = N - 1 ; while (L <= R) { int M = (L + R) / 2 ; if (nums[M] == target) { return M; } if (nums[L] == nums[M] && nums[M] == nums[R]) { while (L != M && nums[L] == nums[M]) { L++; } if (L == M) { L = M + 1 ; continue ; } } if (nums[L] != nums[M]) { if (nums[L] < nums[M]) { if (nums[L] <= target && target < nums[M]) { R = M - 1 ; } else { L = M + 1 ; } } else { if (nums[M] < target && target <= nums[R]) { L = M + 1 ; } else { R = M - 1 ; } } } else { if (nums[M] < nums[R]) { if (nums[M] < target && target <= nums[R]) { L = M + 1 ; } else { R = M - 1 ; } } else { if (nums[L] <= target && target < nums[M]) { R = M - 1 ; } else { L = M + 1 ; } } } } return -1 ; }
合并两个有序数组
给你两个有序数组 nums1 和 nums2,另有两个整数 m 和 n ,分别表示 nums1 和 nums2 中的元素数目。进行合并。
注意:最终,合并后数组不应由函数返回,而是存储在数组 nums1 中。nums1 的初始长度为 m + n,其中前 m 个元素表示应合并的元素,后 n 个元素为 0 ,应忽略。nums2 的长度为 n 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public void merge (int [] nums1, int m, int [] nums2, int n) { int index = nums1.length; while (m > 0 && n > 0 ) { if (nums1[m - 1 ] >= nums2[n -1 ]){ nums1[--index] = nums1[--m]; } else { nums1[--index] = nums2[--n]; } } while (n > 0 ) { nums1[--index] = nums2[--n]; } }
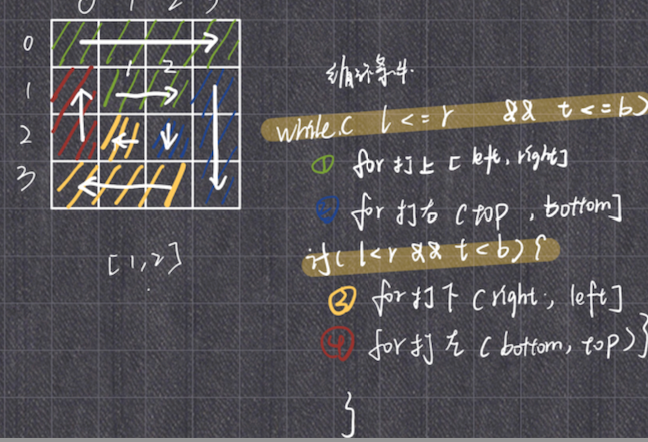
螺旋矩阵
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) { List<Integer> order = new ArrayList <>(); if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0 ].length == 0 ) { return order; } int left = 0 ; int top = 0 ; int right = matrix[0 ].length - 1 ; int bottom = matrix.length - 1 ; while (left <= right && top <= bottom) { for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) { order.add(matrix[top][i]); } for (int i = top + 1 ; i <= bottom; i++) { order.add(matrix[i][right]); } if (right > left && bottom > top) { for (int i = right - 1 ; i >= left; i--) { order.add(matrix[bottom][i]); } for (int i = bottom - 1 ; i > top; i--) { order.add(matrix[i][left]); } } left++; top++; right--; bottom--; } return order; }
字符串相加
给定两个字符串形式的非负整数 num1 和num2 ,计算它们的和并同样以字符串形式返回。
你不能使用任何內建的用于处理大整数的库(比如 BigInteger), 也不能直接将输入的字符串转换为整数形式。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public String addStrings2 (String num1, String num2) { int i = num1.length() - 1 , j = num2.length() - 1 , add = 0 ; StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer (); while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || add != 0 ) { int x = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i) - '0' : 0 ; int y = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j) - '0' : 0 ; int result = x + y + add; ans.append(result % 10 ); add = result / 10 ; i--; j--; } ans.reverse(); return ans.toString(); }
二分查找 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public int search (int [] nums, int target) { int L = 0 ; int R = nums.length - 1 ; while (L < R){ int mid = (L + R) >> 1 ; if (target < nums[mid]){ R = mid - 1 ; } else if (target > nums[mid]){ L = mid + 1 ; } else { return mid; } } return (nums[L] == target) ? L : -1 ; }
在排序数组中找到元素第一个和最后一个位置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public class Fre_044_FindFirstAndLastPositionOfElementInSortedArray { public static int [] searchRange(int [] nums, int target) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) { return new int [] { -1 , -1 }; } int L = lessMostRight(nums, target) + 1 ; if (L == nums.length || nums[L] != target) { return new int [] { -1 , -1 }; } return new int [] { L, lessMostRight(nums, target + 1 ) }; } public static int lessMostRight (int [] arr, int num) { int L = 0 ; int R = arr.length - 1 ; int M = 0 ; int ans = -1 ; while (L <= R) { M = L + ((R - L) >> 1 ); if (arr[M] < num) { ans = M; L = M + 1 ; } else { R = M - 1 ; } } return ans; } }
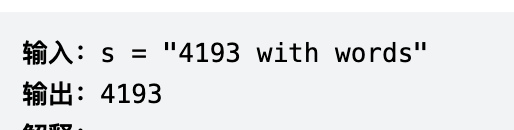
字符串转化整数 注意有很多特殊情况
1.需要删除无用的前导空格
2.检查下一个字符为正还是负
3.只读一开始是数字的部分
4.超出范围的数字返回边界
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 1. 主函数myAtoi(): 1 除去空格和后面非数字的部分( 前后都要判空)【removeHeadZero()】 2 判断该部分是否是有效数字【isValid()】 3 转为负数形式(转回不会溢出,负数范围大些) posi(标志正负) 4 res是最负的情况 (用了负数就只用可以装下,如果用整数转,最小就没法装) 2. removeHeadZero(): 1 是否有符号 2 s标志第一个不是零的位置 3 e标志数字部分后面的非数字部分的开头 4 返回截取的带符号整数部分 3. isVaild(): 判断带符号整数部分是否有效 1 开头在remove部分没有判断,只要开头不是数字和符号都返回无效 2 只有符号也无效 3 夹杂着非数字字符也无效
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 public class Fre_072_StringToInteger { public int myAtoi (String s) { if (s == null || s.equals("" )){ return 0 ; } s = removeHeadZero(s.trim()); if (s == null || s.equals("" )){ return 0 ; } char [] str = s.toCharArray(); if (!isValid(str)){ return 0 ; } boolean posi = str[0 ] == '-' ? false : true ; int minq = Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 ; int minp = Integer.MIN_VALUE % 10 ; int res = 0 ; int cur = 0 ; for (int i = (str[0 ] == '-' || str[0 ] == '+' ) ? 1 : 0 ; i < str.length; i++){ cur = '0' - str[i]; if (res < minq || (res == minq && cur < minp)){ return posi ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : Integer.MIN_VALUE; } res = res * 10 + cur; } if (posi && (res == Integer.MIN_VALUE)){ return Integer.MAX_VALUE; } return posi ? -res : res; } public static String removeHeadZero (String s) { boolean r = (s.startsWith("+" ) || s.startsWith("-" )); int start = r ? 1 : 0 ; for (; start< s.length(); start++){ if (s.charAt(start) != '0' ){ break ; } } int e = -1 ; for (int i = s.length() - 1 ; i >= (r ? 1 : 0 ); i--){ if (s.charAt(i) < '0' || s.charAt(i) > '9' ) { e = i; } } return (r ? String.valueOf(s.charAt(0 )): "" ) + s.substring(start, e == -1 ? s.length() : e); } public static boolean isValid (char [] str) { if (str[0 ] != '-' && str[0 ] != '+' && (str[0 ] < '0' || str[0 ] > '9' )){ return false ; } if ((str[0 ] == '-' || str[0 ] == '+' ) && str.length == 1 ){ return false ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < str.length; i++){ if (str[i] <'0' || str[i] > '9' ){ return false ; } } return true ; } }
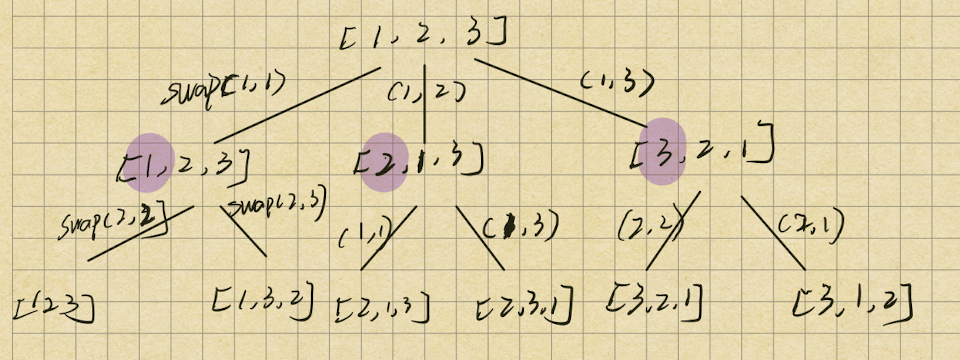
下一个排列
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找出 nums 的字典序中的下一个排列。
例如,arr = [1,2,3] 的下一个排列是 [1,3,2] 。
必须 原地 修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public void nextPermutation (int [] nums) { int i = nums.length - 2 ; while (i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1 ]) { i--; } if (i >= 0 ){ int j = nums.length - 1 ; while (nums[i] >= nums[j]){ j--; } swap(nums, i, j); } reverse(nums, i + 1 ); } public static void reverse (int [] nums, int i) { int left = i; int right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left < right){ swap(nums, left, right); left++; right--; } } public static void swap (int [] nums, int i, int j) { int tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = tmp; }
合并区间
以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回 一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间 。
s 和 e 记录上一个区间的边界
然后复用interval数组来存储,最后复制数组size部分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { if (intervals.length == 0 ) { return new int [0 ][0 ]; } Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0 ] - b[0 ]); int s = intervals[0 ][0 ]; int e = intervals[0 ][1 ]; int size = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++) { if (intervals[i][0 ] > e) { intervals[size][0 ] = s; intervals[size++][1 ] = e; s = intervals[i][0 ]; e = intervals[i][1 ]; } else { e = Math.max(e, intervals[i][1 ]); } } intervals[size][0 ] = s; intervals[size++][1 ] = e; return Arrays.copyOf(intervals, size); } }
x的平方根 ==二分查找==
给你一个非负整数 x ,计算并返回 x 的 算术平方根 。
由于返回类型是整数,结果只保留 整数部分 ,小数部分将被 舍去 。
注意:不允许使用任何内置指数函数和算符,例如 pow(x, 0.5) 或者 x ** 0.5 。
1 2 1. 使用 二分 <=就更新ans和L 到右边就更新R 2. 注意数据类型时long主要是为了两个整型相乘不会溢出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public static int mySqrt (int x) { if (x == 0 ) { return 0 ; } if (x < 3 ) { return 1 ; } long ans = 1 ; long L = 1 ; long R = x; long M = 0 ; while (L <= R) { M = (L + R) / 2 ; if (M * M <= x) { ans = M; L = M + 1 ; } else { R = M - 1 ; } } return (int ) ans; }
扩展:求出小数点后k位 其实思路与一样 只是换成double类型并且需要转换数格式
缺失的正数
给你一个未排序的整数数组,请你找出没有出现的最小的正整数 时间复杂度o(n)
除了打标记以外,我们还可以使用置换的方法,将给定的数组「恢复」成下面的形式:
如果数组中包含 x∈[1,N]x \in [1, N]x∈[1,N],那么恢复后,数组的第 x−1x - 1x−1 个元素为 xxx。
在恢复后,数组应当有 [1, 2, …, N] 的形式,但其中有若干个位置上的数是错误的,每一个错误的位置就代表了一个缺失的正数。以题目中的示例二 [3, 4, -1, 1] 为例,恢复后的数组应当为 [1, -1, 3, 4],我们就可以知道缺失的数为 2。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public int firstMissingPositive (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= n && nums[nums[i] - 1 ] != nums[i]) { int temp = nums[nums[i] - 1 ]; nums[nums[i] - 1 ] = nums[i]; nums[i] = temp; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { if (nums[i] != i + 1 ) { return i + 1 ; } } return n + 1 ; }
用rand7()生成rand10()
用一个不等概率返回0和1的函数, 怎么加工一个函数0和1等概率返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public int rand10 () { int ans= 0 ; do { ans = f2(); }while (ans >9 ); return ans + 1 ; } public int f () { int ans= 0 ; do { ans = rand7(); }while (ans == 4 ); return ans < 4 ? 0 :1 ; } public int f2 () { return (f() << 3 ) + (f() << 2 ) + (f() << 1 )+ f(); }
找到两个有序数组的中位数(⚠️)/两个有序数组第k小 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 public double findMedianSortedArrays (int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int size = nums1.length + nums2.length; boolean e = (size & 1 ) == 0 ; if (nums1.length == 0 && nums2.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; }else if (nums1.length == 0 ){ if (!e){ return nums2[size/ 2 ]; }else { return (double )(nums2[ size / 2 - 1 ] + nums2[size / 2 ])/2 ; } }else if (nums2.length == 0 ){ if (!e){ return nums1[size/ 2 ]; }else { return (double )(nums1[size / 2 - 1 ] + nums1[size / 2 ])/2 ; } }else { if (!e){ return findKthNum(nums1, nums2, size / 2 + 1 ); }else { return (double )(findKthNum(nums1, nums2, size/2 )+findKthNum(nums1, nums2, size/2 +1 ))/2D ; } } public static int getUpMedian (int [] arr1, int s1,int e1,int [] arr2, int s2, int e2) { int mid1 = 0 ; int mid2 = 0 ; while (s1 < e1){ mid1 = (e1 + s1) >> 1 ; mid2 = (e2 + s2) >> 1 ; if (arr1[mid1] == arr2[mid2] ) return arr1[mid1]; if (((e1 - s1 + 1 ) & 1 ) == 1 ){ if (arr1[mid1] < arr2[mid2]){ if (arr1[mid1] >= arr2[mid2 - 1 ]) return arr1[mid1]; s1 = mid1 + 1 ; e2 = mid2 - 1 ; }else { if (arr2[mid2] >= arr1[mid1 - 1 ]) return arr2[mid2]; s2 = mid2 + 1 ; e1 = mid1 - 1 ; } } else { if (arr1[mid1] > arr2[mid2]){ e1 = mid1; s2 = mid2 + 1 ; }else { e2 = mid2; s1 = mid1 + 1 ; } } } return Math.min(arr1[s1], arr2[s2]); } public static int findKthNum (int [] arr1, int [] arr2, int k) { int [] longs = arr1.length >= arr2.length ? arr1 : arr2; int [] shorts = arr1.length < arr2.length ? arr1 : arr2; int l = longs.length; int s = shorts.length; if (k <= s){ return getUpMedian(longs, 0 , k - 1 , shorts, 0 , k - 1 ); } if (k > l){ if (longs[k - s - 1 ] >= shorts[s - 1 ]){ return longs[k - s -1 ]; } if (shorts[k - l - 1 ] >= longs[l - 1 ]){ return shorts[k - l - 1 ]; } return getUpMedian(longs, k - s, l - 1 , shorts, k - l, s - 1 ); } if (longs[k - s - 1 ] >= shorts[s - 1 ]){ return longs[k - s - 1 ]; } return getUpMedian(longs, k - s, k - 1 ,shorts, 0 ,s - 1 ); }
翻转字符串中的单词
给你一个字符串 s ,逐个翻转字符串中的所有 单词 。
单词 是由非空格字符组成的字符串。s 中使用至少一个空格将字符串中的 单词 分隔开。
请你返回一个翻转 s 中单词顺序并用单个空格相连的字符串。
说明:
输入字符串 s 可以在前面、后面或者单词间包含多余的空格。
示例 1:
输入:s = “the sky is blue”
示例 2:
输入:s = “ hello world “
思路:
去除多余的空白: **(1去掉字符串开头的空白字符**
**(2去掉字符串末尾的空白字符**
**(3将字符串间多余的空白字符去除**
翻转字符串:
翻转每一个单词: **(1 遍历sb 使用start 和 end来抓单词**
**(2 翻转单词**
**(3 更新start,去找下一个单词**
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 public String reverseWords (String s) { StringBuilder sb = trimSpaces(s); reverse(sb, 0 , sb.length() - 1 ); reverseEachWord(sb); return sb.toString(); } public StringBuilder trimSpaces (String s) { int left = 0 , right = s.length() - 1 ; while (left <= right && s.charAt(left) == ' ' ) { ++left; } while (left <= right && s.charAt(right) == ' ' ) { --right; } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); while (left <= right) { char c = s.charAt(left); if (c != ' ' ) { sb.append(c); } else if (sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1 ) != ' ' ) { sb.append(c); } ++left; } return sb; } public void reverse (StringBuilder sb, int left, int right) { while (left < right) { char tmp = sb.charAt(left); sb.setCharAt(left++, sb.charAt(right)); sb.setCharAt(right--, tmp); } } public void reverseEachWord (StringBuilder sb) { int n = sb.length(); int start = 0 , end = 0 ; while (start < n) { while (end < n && sb.charAt(end) != ' ' ) { ++end; } reverse(sb, start, end - 1 ); start = end + 1 ; ++end; } }
字符串相乘
给定两个以字符串形式表示的非负整数 num1 和 num2,返回 num1 和 num2 的乘积,它们的乘积也表示为字符串形式。
注意:不能使用任何内置的 BigInteger 库或直接将输入转换为整数。
示例 1:
输入: num1 = “2”, num2 = “3”
示例 2:
输入: num1 = “123”, num2 = “456”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public String multiply (String num1, String num2) { if (num1.equals("0" ) || num2.equals("0" )) { return "0" ; } int m = num1.length(), n = num2.length(); int [] ansArr = new int [m + n]; for (int i = m - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int x = num1.charAt(i) - '0' ; for (int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { int y = num2.charAt(j) - '0' ; ansArr[i + j + 1 ] += x * y; } } for (int i = m + n - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { ansArr[i - 1 ] += ansArr[i] /10 ; ansArr[i] %= 10 ; } int index = ansArr[0 ] == 0 ? 1 : 0 ; StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer (); while (index < m + n) { ans.append(ansArr[index]); index++; } return ans.toString(); }
删除数组中的重复项 任何删除重复的都可以用快慢指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Fre_017_RemoveDuplicatesFromSortedArray { public static int removeDuplicates (int [] nums) { if (nums == null ) { return 0 ; } if (nums.length < 2 ) { return nums.length; } int done = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] != nums[done]) { nums[++done] = nums[i]; } } return done + 1 ; } }
去除重复字母 贪心➕单调栈?
给你一个字符串 s ,请你去除字符串中重复的字母,使得每个字母只出现一次。需保证 返回结果的字典序最小(要求不能打乱其他字符的相对位置)。
示例 1:
输入:s = “bcabc”
示例 2:
输入:s = “cbacdcbc”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public String removeDuplicateLetters (String s) { boolean [] vis = new boolean [26 ]; int [] num = new int [26 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { num[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ]++; } StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer (); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { char ch = s.charAt(i); if (!vis[ch - 'a' ]) { while (sb.length() > 0 && sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1 ) > ch) { if (num[sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1 ) - 'a' ] > 0 ) { vis[sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1 ) - 'a' ] = false ; sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1 ); } else { break ; } } vis[ch - 'a' ] = true ; sb.append(ch); } num[ch - 'a' ] -= 1 ; } return sb.toString(); }
单词搜索
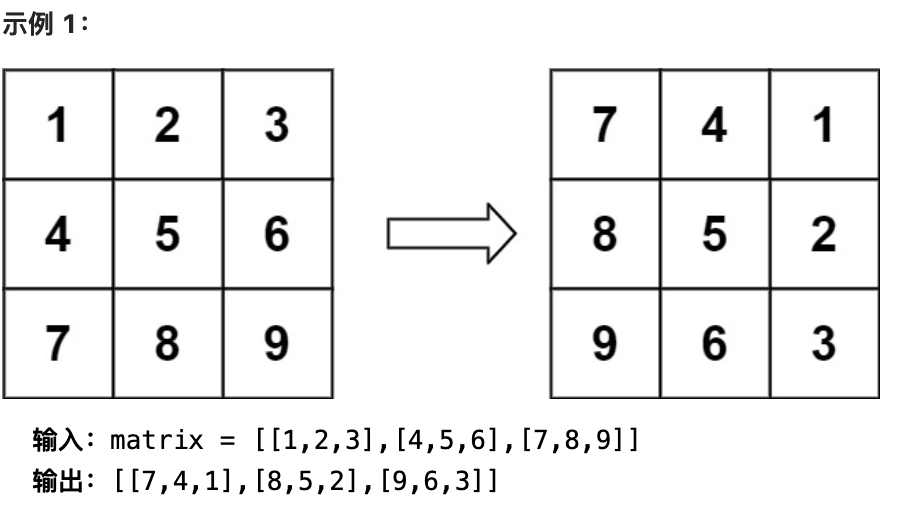
给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵 matrix 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。
你必须在 原地 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要 使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public void rotate (int [][] matrix) { int a = 0 ; int b = 0 ; int c = matrix.length - 1 ; int d = matrix[0 ].length - 1 ; while (a < c) { rotateEdge(matrix, a++, b++, c--, d--); } } public static void rotateEdge (int [][] m, int a, int b, int c, int d) { int tmp = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < d - b; i++) { tmp = m[a][b + i]; m[a][b + i] = m[c - i][b]; m[c - i][b] = m[c][d - i]; m[c][d - i] = m[a + i][d]; m[a + i][d] = tmp; } }
多数元素
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的多数元素。多数元素是指在数组中出现次数 大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。
你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。
是一个超级水王问题
1 2 3 1遍历 使用 candidate和HP 来一次删除两个不同的数 2到最后 HP 不为0 则说明可能有水王 是当前的candidate 3再遍历一次找candi 如果 HP> n/2 说明就是水王
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public int majorityElement (int [] nums) { if (nums == null ) { return -1 ; } int n = nums.length; int candi = 0 ; int HP = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (HP == 0 ) { candi = nums[i]; HP++; }else if ( nums[i] != candi) { HP--; }else { HP++; } } if (HP == 0 ) { return -1 ; } HP = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) { if (nums[i] == candi) { HP++; } } if (HP > n / 2 ) { return candi; } else { return -1 ; } } }
1 链表 1 反转链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null ) { ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; }
反转链表二
就是反转链表中间一截
// 第 1 步:从虚拟头节点走 left - 1 步,来到 left 节点的前一个节点
// 第 2 步:从 pre 再走 right - left + 1 步,来到 right 节点
// 第 3 步:切断出一个子链表(截取链表)先标记再切断
// 第 4 步:[同反转链表](##1 反转链表##),反转链表的子区间
// 第 5 步:接回到原来的链表中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 public ListNode reverseBetween (ListNode head, int left, int right) { ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode (-1 ); dummyNode.next = head; ListNode pre = dummyNode; for (int i = 0 ; i < left - 1 ;i++) { pre = pre.next; } ListNode rNode = pre; for (int i = 0 ; i < right - left + 1 ;i++) { rNode = rNode.next; } ListNode lNode = pre.next; ListNode end = rNode.next; pre.next = null ; rNode.next = null ; reverseLinkedList(lNode); pre.next = rNode; lNode.next = end; return dummyNode.next; } private void reverseLinkedList (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null ) { ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } }
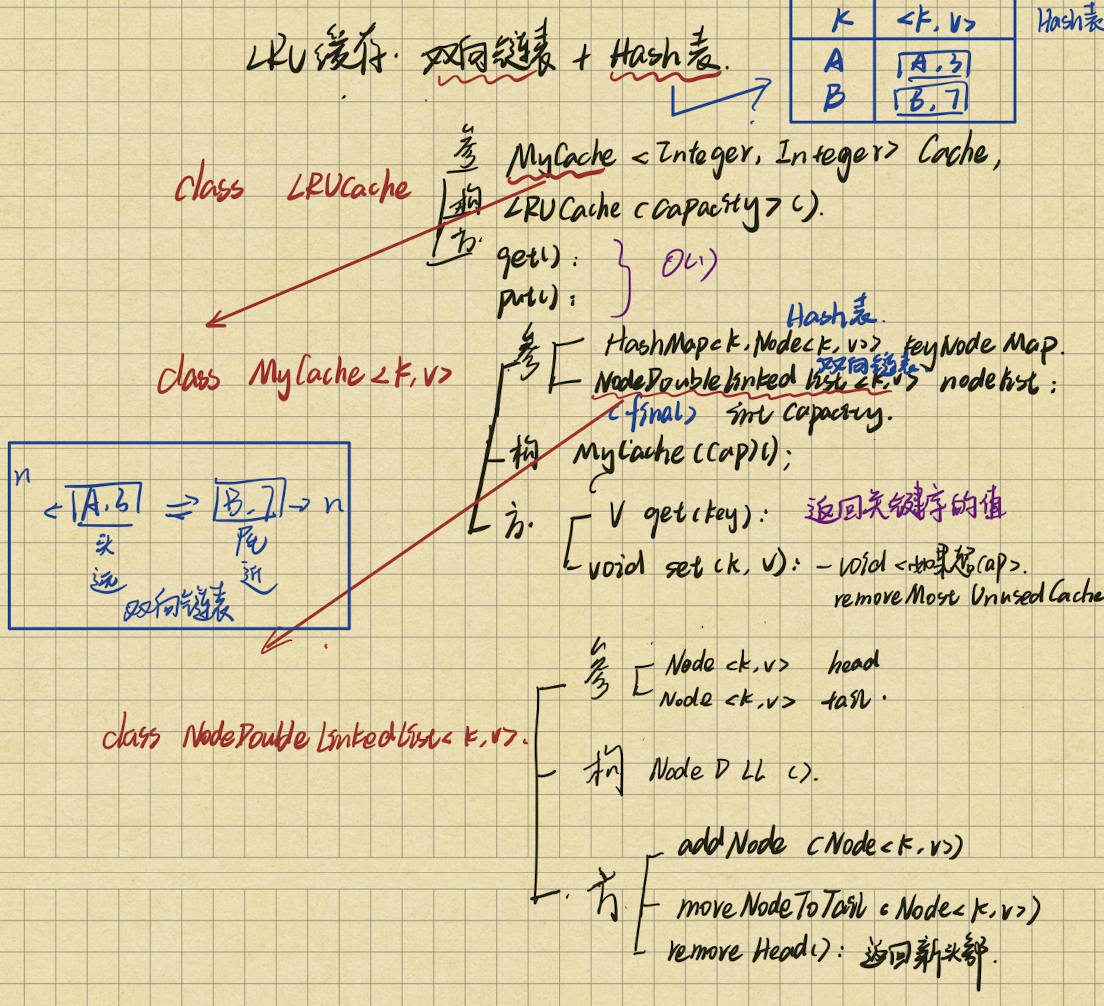
2 LRU缓存机制
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
LRUCache(int capacity) 以 正整数 作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存
函数 get 和 put 必0须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
1) 总的缓存结构 和方法调用 构造方法 1 2 3 4 5 private MyCache<Integer, Integer> cache; public Fre_278_LRUCache (int capacity) { cache = new MyCache <>(capacity); }
1 get() 1 2 3 4 public int get (int key) { Integer ans = cache.get(key); return ans = = null ? -1 : ans; }
2 put() 1 2 3 public void put (int key, int value) { cache.set(key, value); }
2)MyCache 构造方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static class MyCache <K, V> { private HashMap<K, Node<K, V>> keyNodeMap; private NodeDoubleLinkedList<K, V> nodeList; private final int capacity; public MyCache (int cap) { keyNodeMap = new HashMap <K, Node<K, V>>(); nodeList = new NodeDoubleLinkedList <K, V>(); capacity = cap; }
1 V get(K key) 通过key返回value 需要将node放到尾部 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public V get (K key) { if (keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) { Node<K, V> res = keyNodeMap.get(key); nodeList.moveNodeToTail(res); return res.value; } return null ; }
2 void set(K key, V value) 更新与新增:放到尾部,超出内存就删除最长时间没有操作的 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public void set (K key, V value) { if (keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) { Node<K, V> node = keyNodeMap.get(key); node.value = value; nodeList.moveNodeToTail(node); } else { Node<K, V> newNode = new Node <K, V>(key, value); keyNodeMap.put(key, newNode); nodeList.addNode(newNode); if (keyNodeMap.size() == capacity + 1 ) { removeMostUnusedCache(); } } }
3 void removeMostUnusedCache() 删去最长时间没有操作的缓存 ;在两个结构里面都删除 1 2 3 4 private void removeMostUnusedCache () { Node<K, V> removeNode = nodeList.removeHead(); keyNodeMap.remove(removeNode.key); }
3) 双向链表结构 基于LRU机制的双向链表结构
构造方法 :将头尾置为空
1 2 3 4 public NodeDoubleLinkedList(){ head = null; tail = null; }
1 addNode() : 来新节点,挂到尾巴上 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public void addNode (Node<K, V> newNode) { if (newNode == null ) { return ; } if (head == null ) { head = newNode; tail = newNode; } else { tail.next = newNode; newNode.last = tail; tail = newNode; } }
2 moveToTail() : (修改过的节点,要保证node在表中)更新到尾部 1 2 3 public void moveNodeToTail (Node<K, V> node) { }
3 removeHead() : 将头节点移走,返回新的头节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public static class NodeDoubleLinkedList <K, V> { public Node<K, V> removeHead () { if (head == null ) { return null ; } Node<K, V> res = head; if (head == tail) { head = null ; tail = null ; } else { head = res.next; res.next = null ; head.last = null ; } return res; } }
3 K个一组翻转链表 1 先将第一组k凑齐 并且反转
(1)更新start (2)更新end 注意判空!!
(3) 反转 :end 变头
(4) 上一组结尾连接到现在的开头end (5)更新lastEnd
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) { ListNode start = head; ListNode end = getKEnd(start, k); if (end == null ) { return head; } head = end; reverse(start, end); ListNode lastEnd = start; while (lastEnd.next != null ) { start = lastEnd.next; end = getKEnd(start, k); if (end == null ) { return head; } reverse(start, end); lastEnd.next = end; lastEnd = start; } return head; } private ListNode getKEnd (ListNode start, int k) { while (--k != 0 && start != null ) { start = start.next; } return start; } private void reverse (ListNode start, ListNode end) { end = end.next; ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = start; ListNode next = null ; while (cur != end) { next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } start.next = end; }
4 合并两个有序链表
先抓小头head
cur2抓大头 cur1 = head.next pre = head
比较 c1 c2 谁小pre的next就指向谁 并且cur pre 后移
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public static ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { if (l1 == null || l2 ==null ){ return l1 = = null ? l2 : l1; } ListNode head = l1.val <= l2.val ? l1 : l2; ListNode cur1 = head.next; ListNode cur2 = head == l1 ? l2 : l1; ListNode pre = head; while (cur1 != null && cur2 != null ){ if (cur1.val <= cur2.val){ pre.next = cur1; cur1 = cur1.next; }else { pre.next = cur2; cur2 = cur2.next; } pre = pre.next; } pre.next = cur1 != null ? cur1 :cur2; return head; }
合并k个链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public class LianBiao_MergeMoreList { public static class ListNodeComparator implements Comparator <ListNode> { @Override public int compare (ListNode arg0, ListNode arg1) { return arg0.val - arg1.val; } } public ListNode mergeKLists (ListNode[] lists) { if (lists == null ) { return null ; } PriorityQueue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue <>( new ListNodeComparator ()); for (int i = 0 ; i < lists.length; i++) { if (lists[i] != null ) { heap.add(lists[i]); } } if (heap.isEmpty()){ return null ; } ListNode head = heap.poll(); if (head.next != null ) { heap.add(head.next); } ListNode pre = head; while (!heap.isEmpty()) { ListNode cur = heap.poll(); pre.next = cur; pre = cur; if (cur.next != null ) { heap.add(cur.next); } } return head; } }
5 相交链表 需要分有环和无环两种情况 [如何辨别有无环](##6 环形链表##)
无环链表相交
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
需要两个指针;
先用n记录两个链表长度大小以便分清楚谁长谁短,n长度差记得取绝对值;
长的走n步到和短的一样长的起点;
两个指针一起走到相等的地方 就是交点 返回;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public static ListNode getNoLoop (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null ){ return null ; } ListNode cur1 = headA; ListNode cur2 = headB; int n = 0 ; while (cur1 != null ){ n++; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur2 != null ){ n--; cur2 = cur2.next; } if (cur1 != cur2){ return null ; } cur1 = n > 0 ? headA : headB; cur2 = (cur1 == headA) ? headB : headA; n = Math.abs(n); while (n != 0 ){ n--; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur1 != cur2){ cur1 = cur1.next; cur2 = cur2.next; } return cur1; }
有环链表相交 有环的链表比较复杂 有三种情况
1 两个入环节点相同 即相交在入环前 (loop1 =loop2)
2 两个相交在环内相交 有两个相交点
3 两个不相交
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public static ListNode bothLoop (ListNode headA,ListNode loop1,ListNode headB, ListNode loop2) { ListNode cur1 = null ; ListNode cur2 = null ; if (loop1 == loop2){ cur1 = headA; cur2 = headB; int n = 0 ; while (cur1 != loop1){ n++; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur2 != loop2){ n--; cur2 = cur2.next; } if (cur1 != cur2){ return null ; } cur1 = n > 0 ? headA : headB; cur2 = (cur1 == headA) ? headB : headA; n = Math.abs(n); while (n != 0 ){ n--; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur1 != cur2){ cur1 = cur1.next; cur2 = cur2.next; } return cur1; }else { cur1 = loop1.next; while (cur1 != loop1){ if (cur1 == loop2){ return loop1; } } return null ; } }
6 环形链表
返回入环节点,没有环就返回null;
1.先将从头节点快慢指针开始往后,如果两个指针相遇那一定有环,期间如果快指针到null,可以直接判断无环。
2.如果要找到入环节点,就将fast指针指向head,slow不动,然后让两个指针都只移动一步,最后一定会在入环处相遇。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public static ListNode hasCycle (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null ){ return null ; } ListNode slow = head.next; ListNode fast = head.next.next; while (slow != fast){ if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null ){ return null ; } fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } fast = head; while (slow != fast){ fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow; }
7 重排链表
给定一个单链表 L 的头节点 head ,单链表 L 表示为:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln
请将其重新排列后变为:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …
不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
找到原表的中点
快慢指针从head开走
fast.next == null || fast.next.next = null 返回慢指针
将右半端反转:[反转链表](##1 反转链表##)
将左右端合并
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public void reorderList (ListNode head) { public void reorderList (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return ; } ListNode mid = middleNode(head); ListNode l1 = head; ListNode l2 = mid.next; mid.next =null ; l2 = reverse(l2); mergeList(l1, l2); } public ListNode middleNode (ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow; } public ListNode reverse (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null ) { ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; } public void mergeList (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode l1_next; ListNode l2_next; while (l1 != null && l2 != null ) { l1_next = l1.next; l2_next = l2.next; l1.next = l2; l1 = l1_next; l2.next = l1; l2 = l2_next; } } }
8 删除链表重复节点 设置虚拟节点
往后遍历 (条件:cur的下一个和下下个都是空)
循环(第一个节点后面的节点是否有重复的)cur.next指向不等于该x值的节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return head; } ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 , head); ListNode cur = dummy; while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null ){ if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val){ int x = cur.next.val; while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == x){ cur.next = cur.next.next; } } else { cur = cur.next; } } return dummy.next; }
9 排序链表
就是给链表排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 public static ListNode sortList (ListNode head) { int N = 0 ; ListNode cur = head; while (cur != null ) { N++; cur = cur.next; } ListNode h = head; ListNode teamFirst = head; ListNode pre = null ; for (int len = 1 ; len < N; len <<= 1 ) { while (teamFirst != null ) { ListNode[] f1 = f(teamFirst, len); ListNode[] f2 = merge(f1[0 ], f1[1 ], f1[2 ], f1[3 ]); if (h == teamFirst) { h = f2[0 ]; pre = f2[1 ]; } else { pre.next = f2[0 ]; pre = f2[1 ]; } teamFirst = f1[4 ]; } teamFirst = h; pre = null ; } return h; } public static ListNode[] f(ListNode teamFirst, int len) { ListNode ls = teamFirst; ListNode le = teamFirst; ListNode rs = null ; ListNode re = null ; ListNode next = null ; int pass = 0 ; while (teamFirst != null ) { pass++; if (pass <= len) { le = teamFirst; } if (pass == len + 1 ) { rs = teamFirst; } if (pass > len) { re = teamFirst; } if (pass == (len << 1 )) { break ; } teamFirst = teamFirst.next; } le.next = null ; if (re != null ) { next = re.next; re.next = null ; } return new ListNode [] { ls, le, rs, re, next }; } public static ListNode[] merge(ListNode ls, ListNode le, ListNode rs, ListNode re) { if (rs == null ) { return new ListNode [] { ls, le }; } ListNode head = null ; ListNode pre = null ; ListNode cur = null ; ListNode tail = null ; while (ls != le.next && rs != re.next) { if (ls.val <= rs.val) { cur = ls; ls = ls.next; } else { cur = rs; rs = rs.next; } if (pre == null ) { head = cur; pre = cur; } else { pre.next = cur; pre = cur; } } if (ls != le.next) { while (ls != le.next) { pre.next = ls; pre = ls; tail = ls; ls = ls.next; } } else { while (rs != re.next) { pre.next = rs; pre = rs; tail = rs; rs = rs.next; } } return new ListNode [] { head, tail }; }
10 两数相加
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 public ListNode addTwoNumbers (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode l = listLength(l1) > listLength(l2) ? l1 : l2; ListNode s = (l == l1) ? l2 : l1; ListNode curl = l; ListNode curs = s; int carry = 0 ; int curNum = 0 ; ListNode last = curl; while (curs != null ){ curNum = curs.val + curl.val + carry; carry = curNum / 10 ; curl.val = curNum % 10 ; last = curl; curl = curl.next; curs = curs.next; } while (curl != null ){ curNum = curl.val + carry; carry = curNum / 10 ; curl.val = curNum % 10 ; last = curl; curl = curl.next; } if (carry != 0 ){ last.next = new ListNode (1 ); } return l; } public static int listLength (ListNode l) { int length = 0 ; while (l != null ){ length++; l = l.next; } return length; }
11 链表中倒数第k个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。
例如,一个链表有 6 个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是 1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第 3 个节点是值为 4 的节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class Fre_070_removeNthFromEnd { public ListNode getKthFromEnd (ListNode head, int k) { ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; while (k - 1 != 0 ){ fast = fast.next; k--; } while (fast.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; }
12 删除链表倒数第k个节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode (-1 ); dummy.next = head; ListNode slow = dummy; ListNode fast = head; for (;n>0 ;n--){ fast=fast.next; } while (fast != null ){ fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } slow.next = slow.next.next; return dummy.next; }
13 回文链表 需要convert 和 然后判断对称 然后再convert恢复回去
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public boolean isPalindrome (ListNode head) { ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ){ slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } ListNode l1 = null ; ListNode l2 = slow.next; ListNode l3 = null ; while (l2 != null ){ l3 = l2.next; l2.next = l1; l1 = l2; l2 = l3; } boolean ans = true ; l2 = head; l3 = l1; while (l3 != null ){ if (l2.val != l3.val){ ans = false ; break ; } l2 = l2.next; l3 = l3.next; } l2 = null ; l3 = null ; while (l1 != null ){ l3 = l1.next; l1.next = l2; l2 = l1; l1 = l3; } slow.next = l2; return ans; }
14 删除排序链表中的重复元素
给定一个已排序的链表的头 head , 删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素只出现一次 。返回 已排序的链表 。
删除重复元素 留下一个
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public ListNode deleteDuplicates (ListNode head) { if (head == null ){ return null ; } ListNode ans = head; ListNode left = head; ListNode right = head.next; while ( right != null ) { ListNode next = right.next; if (left.val == right.val) { left.next = next; right.next = null ; } else { left = right; } right = next; } return ans; }
15 复制带有随机指针的链表 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 public class LiaoBiao_copyListWithRandom { public static class Node { public int value; public Node next; public Node rand; public Node (int data) { value = data; } } public static Node copyListWithRandom (Node head) { if (head == null ){ return null ; } Node cur = head; Node next = null ; while (cur != null ){ next = cur.next; cur.next = new Node (cur.value); cur.next.next = next; cur = next; } cur = head; Node curCopy = null ; while (cur != null ){ next = cur.next.next; curCopy = cur.next; curCopy.rand = cur.rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null ; cur = next; } cur = head; Node res = head.next; while (cur != null ){ next = cur.next.next; curCopy = cur.next; curCopy.next = cur.next != null ? cur.next.next : null ; cur = next; } return res; } public static Node copyListWithRandom2 (Node head) { HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap <>(); Node cur = head; while (cur != null ){ map.put(cur, new Node (cur.value)); cur = cur.next; } cur = head; while (cur != null ){ map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next); map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand); cur = cur.next; } return map.get(head); } }
2 动态规划 具体步骤 可以参考[零钱兑换](###2 返回凑齐的所有方法数)
基础问题 背包问题 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public class DP2_knapsack { public static int maxValue (int [] w, int [] v, int bag) { if (w == null || v == null || w.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } return process(w, v, 0 , bag); } public static int process (int [] w, int [] v, int i, int rest) { if (rest < 0 ) { return -1 ; } if (i == w.length) { return 0 ; } int p1 = process(w, v, i + 1 , rest - w[i]); int p2 = process(w, v, i + 1 , rest); if (p1 != -1 ) { p1 += v[i]; } return Math.max(p1, p2); } public static int dp (int [] w, int [] v, int bag) { if (w == null || v == null || w.length != v.length || w.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int N = w.length; int [][] dp = new int [N + 1 ][bag + 1 ]; for (int i = N - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i --){ for (int j = 0 ; j <= bag; j ++){ int ans = 0 ; if (j - w[i] >= 0 ){ ans = dp[i + 1 ][j - w[i]] + v[i]; }else { ans = dp[i + 1 ][j]; } dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i+1 ][j], ans); } } return dp[0 ][bag]; }
1. 最大子数组和 用贪心 只需要一个pre反复更新记录以i为底的最大累加和,然后max存最大的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public static int maxSubArray4 (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 || nums == null ) { return 0 ; } int max = nums[0 ]; int pre = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ pre = Math.max(pre + nums[i], nums[i]); max = Math.max(pre, max); } return max; }
如果需要返回该子数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 int res = nums[0 ], l = 0 , r = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.size(); i++) { if (nums[i - 1 ] < 0 ) { l = i; } nums[i] += max(0 , nums[i - 1 ]); if (res < nums[i]) { r = i; res = nums[i]; } }
2. 买卖股票的最佳时机 maxProfit (1) 从头至尾买一次一股 返回最大利润: 遍历一遍 min标记, max最大利润更新 就是找到最低点和最高点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int prices[]) { int minprice = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int maxprofit = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < prices.length; i++) { if (prices[i] < minprice) { minprice = prices[i]; } else if (prices[i] - minprice > maxprofit) { maxprofit = prices[i] - minprice; } } return maxprofit; } }
(2) 买一股但是可以买无限次 遍历累加所有的爬坡
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public static int maxProfit2 (int [] prices) { if (prices == null || prices.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++){ ans += prices[i] - prices[i - 1 ] >= 0 ? prices[i] - prices[i - 1 ] : 0 ; } return ans; }
3. 最长回文子串 (1) 动态规划O(N^2) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public String longestPalindrome33 (String s) { if (s.length() < 2 ) { return s; } char [] str = s.toCharArray(); int N = str.length; boolean [][] dp = new boolean [N][N]; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { dp[i][i] = true ; } int max = 1 ; int index = 0 ; for (int i = N - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--){ for (int L = 0 ; L < i; L++){ int R = L + N - i; if (str[L] == str[R]){ if (R - L < 3 ){ dp[L][R] = true ; }else { dp[L][R] = dp[L + 1 ][R - 1 ]; } } if (dp[L][R] && R - L + 1 > max){ max = R - L + 1 ; index = L; } } } return s.substring(index, index + max); }
(2) Manacher! 面试讲一讲
假设字符串str长度为N,想返回最长回文子串的长度
时间复杂度O(N)
Manacher算法核心 1)理解回文半径数组
最长回文子串就是我知道可以进行。
最长回文子序列 子序列就是三种情况 L+1 ~R 和 L ~ R-1 和 L +1 ~ R - 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public int longestPalindromeSubseq (String s) { public int longestPalindromeSubseq (String s) { if (s.length() == 0 || s == "" ){ return 0 ; } char [] str = s.toCharArray(); int N = str.length; int [][] dp = new int [N][N]; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++){ dp[i][i] = 1 ; } for (int i = N - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ for (int L = 0 ; L < i; L++){ int R = L + N - i; dp[L][R] = Math.max(dp[L + 1 ][R],dp[L][R - 1 ]); if (str[L] == str[R]){ dp[L][R] = Math.max(dp[L + 1 ][R - 1 ] + 2 , dp[L][R]); } } } return dp[0 ][N - 1 ]; }
4. 最长递增子序列 DP版 O(n^2) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; int maxans = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { dp[i] = 1 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (nums[i] > nums[j]) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1 ); } } maxans = Math.max(maxans, dp[i]); } return maxans; }
二分查找+贪心 O(nlogn) 维护一个end数组存储
end[i] 代表 i+1 长度下子序列的最后下标
len = 递增子序列的长 度 - 1(end数组的下标 )
设当前已求出的最长上升子序列的长度为 len(初始时为1),从前往后遍历数组nums,在遍历到 nums[i] 时:
如果 nums[i] >[len] ,则[++len] = nums[i];
否则,在end数组中[0 ~ len-1]二分查找,找到第一个比 nums[i] 小的数 end[k] ,并更新 end[k+1]=nums[i]。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public static int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 || nums == null ) { return 0 ; } int [] end = new int [nums.length]; end[0 ] = nums[0 ]; int len = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] > end[len]) { end[++len] = nums[i]; } else { int L = 0 ; int R = len - 1 ; int pos = 0 ; while (L <= R) { int mid = (R + L) >> 1 ; if (end[mid] < nums[i]){ pos = mid + 1 ; L = mid + 1 ; }else { R = mid - 1 ; } } end[pos] = nums[i]; } } return len + 1 ; }
5. 接雨水
左右两个指针 left right
左右两个变量存储左右最大的值
每次更新左右任意一边靠着lmax或者rmax的指针的雨水大小
相当于是把每一下标积的水累加。
相当于是从左右两边来进行更新 哪边的max最大就比较那一边的L/R与max大小 累加并且更新最大值
最后返回累加和
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public int trap (int [] arr) { int ans = 0 ; int L = 1 ; int R = arr.length - 2 ; int leftMax = arr[0 ]; int rightMax = arr[arr.length - 1 ];z while (L <= R) { if (leftMax <= rightMax) { ans += Math.max(0 , leftMax - arr[L]); leftMax = Math.max(leftMax, arr[L++]); }else { ans += Math.max(0 , rightMax - arr[R]); rightMax = Math.max(rightMax, arr[R--]); } } return ans; }
6. 最长上升子序列 设当前已求出的最长上升子序列的长度为 len(初始时为1),从前往后遍历数组nums,在遍历到 nums[i] 时:
如果 nums[i] d[len] ,则直接加入到 ddd 数组末尾,并更新 len= len+1;
否则,在 d数组中二分查找,找到第一个比 nums[i] 小的数 d[k] ,并更新 d[k+1]=nums[i].
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public static int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 || nums == null ) { return 0 ; } int [] end = new int [nums.length]; end[0 ] = nums[0 ]; int len = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] > end[len]) { end[++len] = nums[i]; } else { int L = 0 ; int R = len - 1 ; int pos = 0 ; while (L <= R) { int mid = (R + L) >> 1 ; if (end[mid] < nums[i]){ pos = mid + 1 ; L = mid + 1 ; }else { R = mid - 1 ; } } end[pos] = nums[i]; } } return len + 1 ; }
7. 爬楼梯 递归 笔试 状态转移方程 f(n) = f(n - 1) + f(n - 2); —-> 可以看出就是斐波拉契数列
用三个常量所以空间复杂度为O(1)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int climbStairs (int n) { int p = 0 , q = 0 , r = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) { p = q; q = r; r = p + q; } return r; }+ }
矩阵快速幂 o(logn) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class Code4_ClimbStairs { public static int climbStairs (int n) { if (n == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int [][] base = { { 1 , 1 }, { 1 , 0 } }; int [][] res = matrixPower(base, n); return res[0 ][0 ]; } public static int [][] matrixPower(int [][] m, int p) { int [][] res = {{1 , 0 }, {0 ,1 }}; int [][] tmp = m; for (; p != 0 ; p >>= 1 ) { if ((p & 1 ) != 0 ) { res = muliMatrix(res, tmp); } tmp = muliMatrix(tmp, tmp); } return res; } public static int [][] muliMatrix(int [][] m1, int [][] m2) { int [][] res = new int [m1.length][m2[0 ].length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m1.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < m2[0 ].length; j++) { for (int k = 0 ; k < m2.length; k++) { res[i][j] += m1[i][k] * m2[k][j]; } } } return res; }
主要就是注意快速幂里面要先进行 一次方的判断
8. 编辑距离(dp3) DP 样本对应模型:往往用最后的位置来判断可能性 给两个单词,返回第一个单词转换为第二个单词最少的操作数, 有增删改三种操作
(扩展:可以增加a d c分别代表增删改的代价)
根据最后一个位置有四种可能
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class DP3_EditDistance { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { if (word1 == null || word2 == null ) { return 0 ; } char [] str1 = word1.toCharArray(); char [] str2 = word2.toCharArray(); int N = str1.length; int M = str2.length; int [][] dp = new int [N+1 ][M+1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= N; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = i; } for (int i = 0 ; i <= M; i++) { dp[0 ][i] = i; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= M; j++) { if (str1[i- 1 ] == str2[j - 1 ]) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]; } else { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; } dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i- 1 ][j] + 1 , dp[i][j]); dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j - 1 ] + 1 , dp[i][j]); } } return dp[N][M]; }
⚠️ 因为有为0的情况 所以总的就是[0, N] 所以循环范围需要是[0,N] 并且str下标 对应 dp下标 减一
9. 最长公共子序列(dp3) ⚠️填边界的时候先将dp[0][0]填了 防止 i - 1 越界
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public int longestCommonSubsequence (String text1, String text2) { if (text1 == null || text2 == null ) { return 0 ; } char [] str1 = text1.toCharArray(); char [] str2 = text2.toCharArray(); int [][] dp = new int [str1.length][str2.length]; dp[0 ][0 ] = str1[0 ] == str2[0 ] ? 1 : 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < str2.length; i++) { dp[0 ][i] = str1[0 ] == str2[i] ? 1 : dp[0 ][i - 1 ]; } for (int i = 1 ; i < str1.length; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = str1[i] == str2[0 ] ? 1 : dp[i - 1 ][0 ]; } for (int i = 1 ; i < str1.length; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < str2.length; j++) { int p1 = dp[i - 1 ][j]; int p2 = dp[i][j - 1 ]; int p3 = str1[i] == str2[j] ? dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 : dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]; dp[i][j] = Math.max(p1, Math.max(p2, p3)); } } return dp[str1.length - 1 ][str2.length - 1 ]; }
10 最小路径和
m ✖️n 的网格 从左下角走到右下角 怎么走路径最短
⚠️[1, 1] 开始填表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public int minPathSum2 (int [][] grid) { if (grid == null || grid.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int m = grid.length; int n = grid[0 ].length; int [][] dp = new int [m][n]; dp[0 ][0 ] = grid[0 ][0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < m; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + grid[i][0 ]; } for (int j = 1 ; j < n; j++) { dp[0 ][j] = dp[0 ][j - 1 ] + grid[0 ][j]; } for (int i = 1 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < n; j++) { dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]) + grid[i][j]; } } return dp[m - 1 ][n - 1 ]; }
扩展 记录路径也可以开一个字典,应该知道了每个 [i,j] 上一个来源坐标 last, path[(i,j)] = (lasti,lastj),最后用一个死循环输出所有path,当 (i,j) == (0,0 ) 时候退出 然后最后进行一个死循环 就可以将循环打出来了
不同路径
m ✖️n 的网格 从左下角走到右下角 有多少种走法 (方法数)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) { int [][] dp = new int [m][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { dp[0 ][i] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < n; j++) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j]+ dp[i][j - 1 ]; } } return dp[m-1 ][n-1 ]; }
11 最长公共子数组(最长重复子数组)
注意的还是边界 ; 应为需要最开始的状态来依赖 所以要不选择dp外围加一圈 要不就是dp内围循环从1开始
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public int findLength (int [] A, int [] B) { int n = A.length, m = B.length; int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][m + 1 ]; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { for (int j = m - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { dp[i][j] = A[i] == B[j] ? dp[i + 1 ][j + 1 ] + 1 : 0 ; ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i][j]); } } return ans; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public int findLength (int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int [][] dp = new int [nums1.length+1 ][nums2.length+1 ]; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= nums1.length;i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= nums2.length; j++) { dp[i][j] = nums1[i-1 ] == nums2[j-1 ] ? dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 : 0 ; ans = Math.max(dp[i][j], ans); } } return ans; }
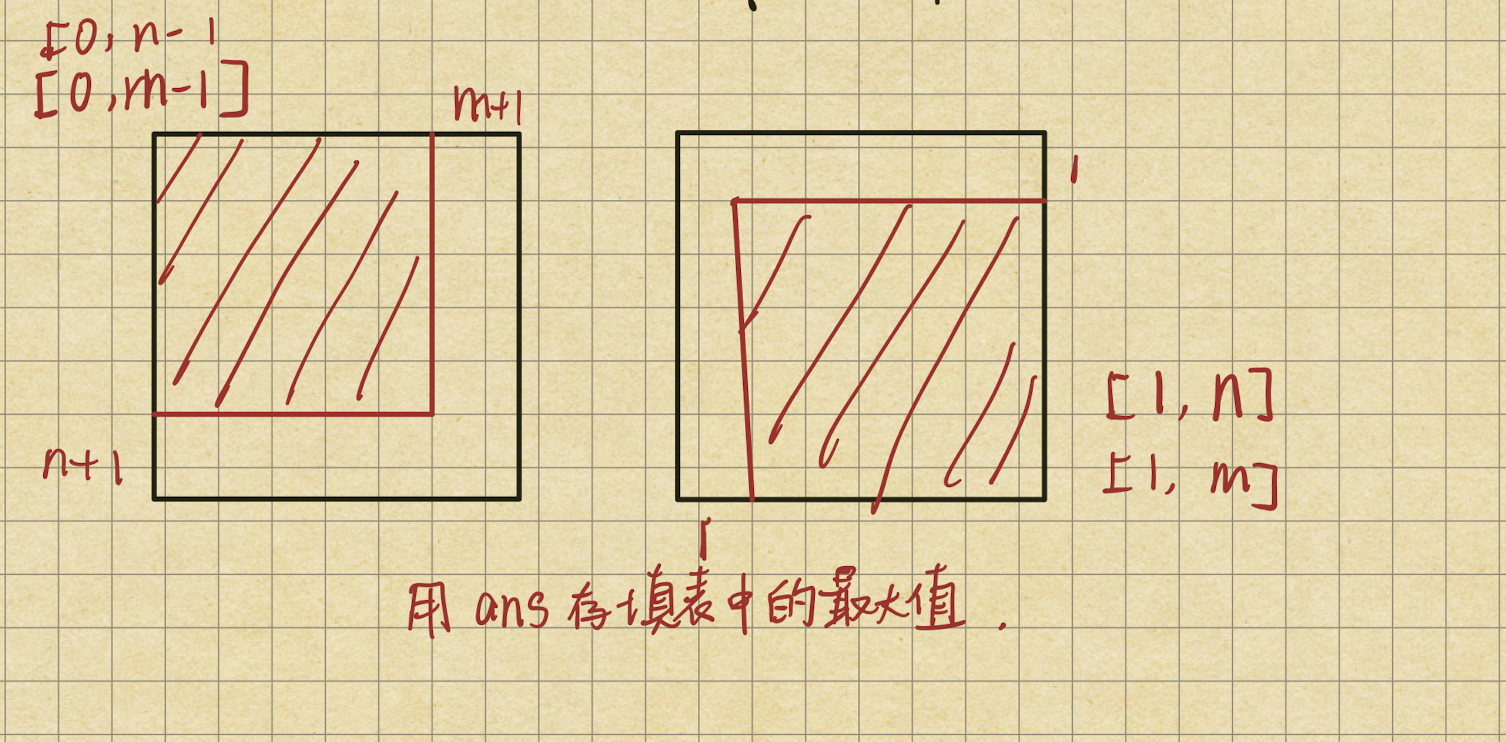
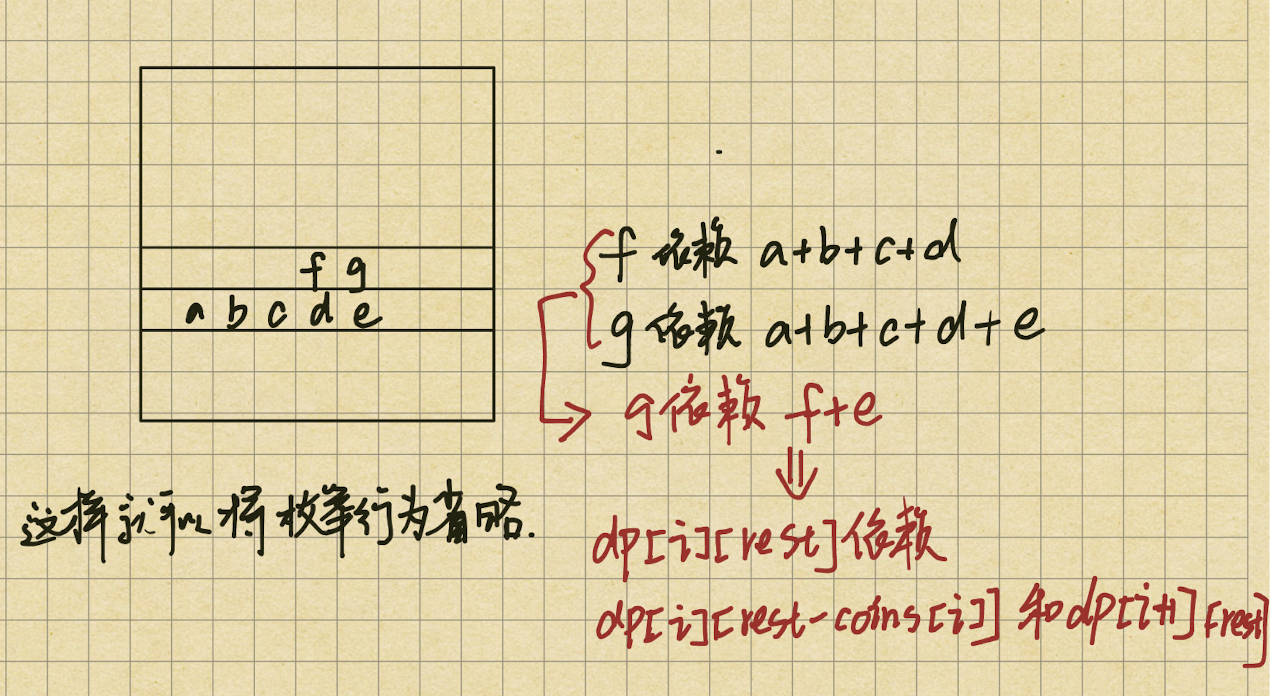
12 零钱兑换问题 <完全背包>(dp4) 难 关于背包问题 吃透背包所有问题
从左向右的尝试模型
给你一个整数数组 coins ,表示不同面额的硬币;以及一个整数 amount ,表示总金额。
1 返回需要最少的硬币个数
计算并返回可以凑成总金额所需的 最少 硬币个数 。
每个硬币都可以说使用无限次。
动态规划 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public int coinChange (int [] arr, int aim) { if (aim == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int N = arr.length; int [][] dp = new int [N + 1 ][aim + 1 ]; dp[N][0 ] = 0 ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= aim; j++) { dp[N][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; } for (int index = N - 1 ; index >= 0 ; index--) { for (int rest = 0 ; rest <= aim; rest++) { dp[index][rest] = dp[index + 1 ][rest]; if (rest - arr[index] >= 0 && dp[index][rest - arr[index]] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) { dp[index][rest] = Math.min(dp[index][rest], dp[index][rest - arr[index]] + 1 ); } } } return dp[0 ][aim] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : dp[0 ][aim]; }
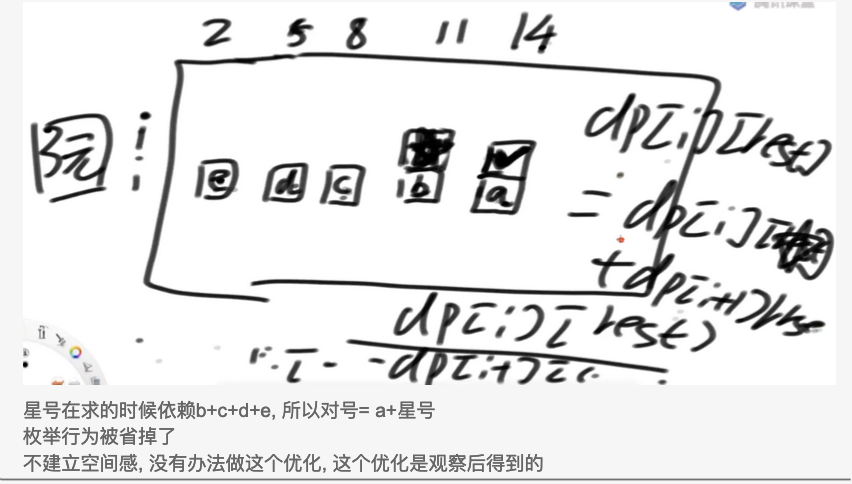
2 返回凑齐的所有方法数
返回硬币或者货币可以凑齐钱的所有方法数
暴力递归的尝试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public static int coinsWay (int [] arr, int aim) { if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0 ) { return 0 ; } return process(arr, 0 , aim); } public static int process (int [] arr, int index, int rest) { if (index == arr.length) { return rest = = 0 ? 1 : 0 ; } int ways = 0 ; for (int zhang = 0 ; zhang * arr[index] <= rest; zhang++) { ways += process(arr, index + 1 , rest - (zhang * arr[index])); } return ways; }
说明是有重复解的 ,所以可以进一步进行记忆化搜索
记忆化搜索 就是用一个结构存储f(i, rest)结果 后面就不会重复解
如果该题没有枚举行为那么傻缓存的方法和严格表结构(动态规划)的方法就是一样的。
严格的表结构 : 就是在记忆化搜索的基础上,进一步梳理了依赖关系,从简单位置算出复杂位置,严格规定好了计算顺序
有枚举行为:需要搞出严格的表结构进行继续优化。
动态规划 第一版dp:有枚举行为,和上面记忆化搜索的方法是等效的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public static int dp1 (int [] arr, int aim) { if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || aim < 0 ) { return 0 ; } int N = arr.length; int [][] dp = new int [N + 1 ][aim + 1 ]; dp[N][0 ] = 1 ; for (int index = N - 1 ; index >= 0 ; index--) { for (int rest = 0 ; rest <= aim; rest++) { int ways = 0 ; for (int zhang = 0 ; zhang * arr[index] <= rest; zhang++) { ways += dp[index + 1 ][rest - (zhang * arr[index])]; } dp[index][rest] = ways; } } return dp[0 ][aim]; }
第二版:将枚举行为的规律找出来,利用严格的表结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public int coinChange (int [] coins, int amount) { if (coins == null || coins.length == 0 || amount < 0 ) { return 0 ; } int N = coins.length; int [][] dp = new int [N + 1 ][amount + 1 ]; dp[N][0 ] = 1 ; for (int index = N - 1 ; index >= 0 ; index--) { for (int rest = 0 ; rest <= amount; rest++) { dp[index][rest] = dp[index + 1 ][rest]; if (rest - coins[index] >= 0 ) { dp[index][rest] += dp[index][rest - coins[index]]; } } } return dp[0 ][amount]; }
3 最终代码 零钱兑换1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public int coinChange (int [] arr, int aim) { if (aim == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int N = arr.length; int [][] dp = new int [N + 1 ][aim + 1 ]; dp[N][0 ] = 0 ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= aim; j++) { dp[N][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; } for (int index = N - 1 ; index >= 0 ; index--) { for (int rest = 0 ; rest <= aim; rest++) { dp[index][rest] = dp[index + 1 ][rest]; if (rest - arr[index] >= 0 && dp[index][rest - arr[index]] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) { dp[index][rest] = Math.min(dp[index][rest], dp[index][rest - arr[index]] + 1 ); } } } return dp[0 ][aim] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : dp[0 ][aim]; } public int coinChange (int [] coins, int amount) { int max = amount + 1 ; int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ]; Arrays.fill(dp, max); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= amount; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < coins.length; j++) { if (coins[j] <= i) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1 ); } } } return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount]; }
零钱兑换2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public int coinChange (int [] coins, int amount) { if (coins == null || coins.length == 0 || amount < 0 ) { return 0 ; } int N = coins.length; int [][] dp = new int [N + 1 ][amount + 1 ]; dp[N][0 ] = 1 ; for (int index = N - 1 ; index >= 0 ; index--) { for (int rest = 0 ; rest <= amount; rest++) { dp[index][rest] = dp[index + 1 ][rest]; if (rest - coins[index] >= 0 ) { dp[index][rest] += dp[index][rest - coins[index]]; } } } return dp[0 ][amount]; } public int change (int amount, int [] coins) { int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; for (int coin : coins) { for (int i = coin; i <= amount; i++) { dp[i] += dp[i - coin]; } } return dp[amount]; }
13 最长有效括号
给你一个只包含 '(' 和 ')' 的字符串,找出最长有效(格式正确且连续)括号子串的长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 思路: 是子串类型,看以i结尾 1 如果当前是‘)’ 就找可以和他配对的最前左括号pre下标 pre = i - dp[i - 1] - 1; (dp[i - 1] 前一个已经配好对的长度 2 如果pre是左括号(注意pre>= 0 防止越界) 更新dp[i] == 2 + dp [i - 1]+ (pre > 0? dp [pre - 1] : 0);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public int longestValidParentheses (String s) { if (s == null || s.length()== 0 ) { return 0 ; } char [] str= s.toCharArray(); int [] dp = new int [s.length()]; int max = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < str.length; i++) { if ( str[i] == ')' ) { int pre = i - dp[i - 1 ] - 1 ; if ( pre >= 0 && str[pre] == '(' ) { dp[i] = 2 + dp[i - 1 ] + (pre > 0 ? dp[pre - 1 ] : 0 ); } } max = Math.max(dp[i], max); } return max; }
14 打家劫舍
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你 不触动警报装置的情况下 ,一夜之内能够偷窃到的最高金额。https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/house-robber
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public int rob (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } if (nums.length == 1 ) { return nums[0 ]; } int n = nums.length; int [] dp = new int [n]; dp[0 ] = nums[0 ]; dp[1 ] = Math.max(dp[0 ], nums[1 ]); for (int i = 2 ; i < n; i++) { int p1 = nums[i]; int p2 = dp[i - 1 ]; int p3 = nums[i] + dp[i - 2 ]; dp[i] = Math.max(p1, Math.max(p2, p3)); } return dp[n - 1 ]; }
打家劫舍Ⅱ
这个地方所有的房屋都 围成一圈 ,这意味着第一个房屋和最后一个房屋是紧挨着的。
是滚动数组,可以分成两个数组来判断[0]-[N-2] 和 [1]-[N-1]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public int rob (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } if (nums.length == 1 ) { return nums[0 ]; } if (nums.length == 2 ) { return Math.max(nums[0 ], nums[1 ]); } int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; dp[0 ] = nums[0 ]; dp[1 ] = Math.max(nums[0 ], nums[1 ]); for (int i = 2 ; i < nums.length-1 ; i++) { int p1 = nums[i]; int p2 = dp[i - 1 ]; int p3 = dp[i - 2 ] + nums[i]; dp[i] = Math.max(p1, Math.max(p2, p3)); } int ans1 = dp[nums.length - 2 ]; dp[1 ] = nums[1 ]; dp[2 ] = Math.max(nums[1 ], nums[2 ]); for (int i = 3 ; i < nums.length; i++) { int p1 = nums[i]; int p2 = dp[i - 1 ]; int p3 = dp[i - 2 ] + nums[i]; dp[i] = Math.max(p1, Math.max(p2, p3)); } int ans2 = dp[nums.length - 1 ]; return Math.max(ans1, ans2); }
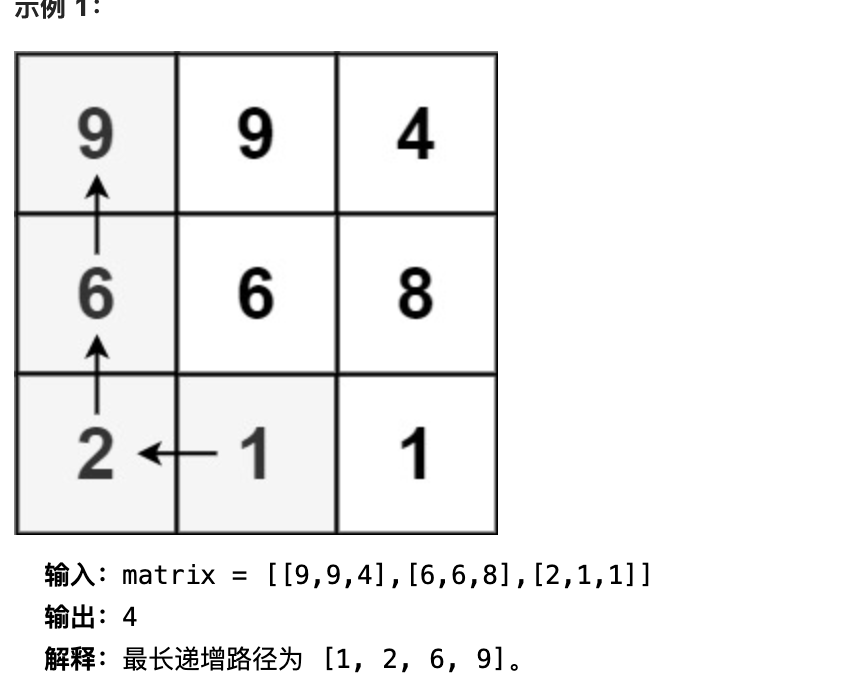
15 矩阵的递增路径
给定一个 m x n 整数矩阵 matrix ,找出其中 最长递增路径 的长度。
对于每个单元格,你可以往上,下,左,右四个方向移动。 你 不能 在 对角线 方向上移动或移动到 边界外(即不允许环绕)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public static int longestIncreasingPath (int [][] matrix) { int ans = 0 ; int N = matrix.length; int M = matrix[0 ].length; int [][] dp = new int [N][M]; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < M; j++) { ans = Math.max(ans, process1(matrix, i, j, dp)); } } return ans; } private static int process1 (int [][] m, int i, int j,int [][] dp) { if (dp[i][j] != 0 ){ return dp[i][j]; } int up = i > 0 && m[i][j] < m[i - 1 ][j] ? process1(m, i - 1 , j, dp) : 0 ; int down = i < (m.length - 1 ) && m[i][j] < m[i + 1 ][j] ? process1(m, i + 1 , j, dp) : 0 ; int left = j > 0 && m[i][j] < m[i][j - 1 ] ? process1(m, i, j - 1 ,dp) : 0 ; int right = j < (m[0 ].length - 1 ) && m[i][j] < m[i][j + 1 ] ? process1( m, i, j + 1 , dp) : 0 ; int ans = Math.max(Math.max(up, down), Math.max(left, right)) + 1 ; dp[i][j] = ans; return ans; }
16 机器人walk 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 public class DP_RobortWalk { public static int way1 (int N, int M, int K, int P) { if (N < 2 || M < 1 || M > N || P < 1 || P > N || K < 1 ) { return -1 ; } return process1(N, M, K, P); } public static int process1 (int n, int cur, int rest, int aim) { if (rest == 0 ){ return cur = = aim ? 1 : 0 ; } if (cur == 1 ){ return process1(n, 2 , rest - 1 , aim); } if (cur == n){ return process1(n, n - 1 , rest - 1 , aim); } return process1(n, cur - 1 , rest - 1 , aim) + process1(n, cur + 1 , rest - 1 , aim); } public static int way3 (int N,int M, int K, int P) { if (N < 2 || M < 1 || M > N || P < 1 || P > N || K < 1 ) { return -1 ; } int [][] dp = new int [N + 1 ][K + 1 ]; dp[P][0 ] = 1 ; for (int rest = 1 ; rest <= K; rest++) { dp[1 ][rest] = dp[2 ][rest - 1 ]; dp[N][rest] = dp[N - 1 ][rest - 1 ]; for (int cur = 2 ; cur < N; cur++) { dp[cur][rest] = dp[cur - 1 ][rest - 1 ] + dp[cur + 1 ][rest - 1 ]; } } return dp[M][K]; } public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println(way1(4 , 2 , 3 , 3 )); System.out.println(way3(4 , 2 , 3 , 3 )); } }
17 纸牌博弈 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public class DP1_TwoSmartManPeekCard { public static int win1 (int [] arr) { if (arr==null ||arr.length==0 ){ return 0 ; } return Math.max(f(arr,0 ,arr.length-1 ), s(arr,0 ,arr.length-1 )) ; } public static int f (int [] arr,int i,int j) { if (i==j){ return arr[i]; } return Math.max(arr[i]+s(arr,i+1 ,j),arr[j]+s(arr,i,j-1 )); } public static int s (int [] arr,int i,int j) { if (i==j){ return 0 ; } return Math.min(f(arr,i+1 ,j),f(arr,i,j-1 )); } public static int win2 (int [] arr) { int N = arr.length; int [][] fmap = new int [N][N]; int [][] gmap = new int [N][N]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= N - 1 ; i++){ fmap[i][i] = arr[i]; } for (int startCol = 1 ; startCol < N; startCol++) { int L = 0 ; int R = startCol; while (R < N) { fmap[L][R] = Math.max(arr[L] + gmap[L + 1 ][R], arr[R] + gmap[L][R - 1 ]); gmap[L][R] = Math.min(fmap[L + 1 ][R], fmap[L][R - 1 ]); L++; R++; } } return Math.max(fmap[0 ][N - 1 ], gmap[0 ][N-1 ]); } }
3 排序 -快速排序- 1.0 partition
partition 以arr[R] 为界分为 <=arr[R] arr[R] >arr[R] 三个部分
每次可以找到一个位置的数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public static int partition (int [] arr, int L, int R) { if (L > R) { return -1 ; } if (L == R) { return L; } int lessEqual = L - 1 ; int index = L; while (index < R) { if (arr[index] <= arr[R]) { swap(arr, index, ++lessEqual); } index++; } swap(arr, ++lessEqual, R); return lessEqual; } public static void quickSort1 (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } process1(arr, 0 , arr.length - 1 ); } public static void process1 (int [] arr, int L, int R) { if (L >= R) { return ; } int M = partition(arr, L, R); process1(arr, L, M - 1 ); process1(arr, M + 1 , R); }
2.0 荷兰国旗
在[l, r]上以arr[R]为界 将数组分为< = > 三个部分
每次可以找到中间等等于那部分的数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public static int [] netherlandsFlag(int [] arr, int L, int R) { if (L > R) {return new int []{-1 , -1 };} if (L == R) {return new int []{L, R};} int less = L - 1 ; int index = L; int more = R; while (index < more) { if (arr[index] == arr[R]) { index++; } else if (arr[index] < arr[R]) { swap(arr, index, ++less); index++; } else { swap(arr, index, --more); } } swap(arr, R, more); return new int []{ less+1 , more}; }
随机快排
在荷兰国旗基础上 将数组的arr[R]进行随机交换 然后递归将数组所有部分都排完
最终期望求出来的复杂度就是O(logN*N)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static void quickSort (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 ) { return ; } process(arr, 0 , arr.length - 1 ); } public static void proces (int [] arr, int L, int R) { if (L > R) {return ;} int random = L + Math.random() * (R - L + 1 ); swap(arr, R, random); int [] area = netherlandsFlag(arr, L, R); process(arr, L, area[0 ] - 1 ); process(arr, area[1 ] + 1 , R); }
递归版本
迭代,自己压栈,把任务做了然后再放出来
最开始做一次递归里做的 然后在迭代过程中再做递归里做的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public static class Op { public int L; public int R; public Op (int left, int right) { L = left; R = right; } } public static void quickSort2 (int [] arr) { if (...) {return ;} int N = arr.length; int random = (int )(Math.random() * N); swap(arr, N - 1 , random); int [] area = netherlandsFlag(arr, 0 , N - 1 ); Stack<Op> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(new Op (0 , area[0 ]-1 )); stack.push(new Op (area[1 ]+1 , N - 1 )); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Op op = stack.pop(); if (op.L < op.R) { random = op.L + (int )(Math.random() * (op.R - op.L + 1 )); swap(arr, op.R, random); area = netherlandsFlag(arr, op.L, op.R); stack.push(new Op (op.L, area[0 ]-1 )); stack.push(new Op (area[1 ]+1 , op.R)); } } }
<随机快排的时间复杂度分析> 1)通过分析知道,划分值越靠近中间,性能越好;越靠近两边,性能越差
时间复杂度O(N logN),额外空间复杂度O(logN)都是这么来的。
!!! ==找到数组中的第k个最大元素== ⚠️是k大还是k小
时间复杂度O(N)
1 原先数组不能改变 复制一个新数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public int findKthLargest (int [] array, int k) { int [] arr = copyArray(array); return process2(arr, 0 , arr.length - 1 , arr.length - k); } public static int process2 (int [] arr, int L, int R, int index) { if (L == R) { return arr[L]; } int random = L + (int )(Math.random() * (R - L + 1 )); int [] area = partition(arr, L, R, arr[random]); if (index >= area[0 ] && index <= area[1 ]) { return arr[index]; } else if (index < area[0 ]) { return process2(arr, L, area[0 ] - 1 , index); } else { return process2(arr, area[1 ] + 1 , R, index); } }
注意这里的partition
因为是使用num来分区 所以边界注意⚠️对比快排用arr[R]来分区
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public static int [] partition(int [] arr, int L , int R, int num) { int less = L - 1 ; int more = R + 1 ; int index = L; while (index < more) { if (arr[index] < num) { swap(arr, index, ++less); index++; }else if (arr[index] > num) { swap(arr, index, --more); }else { index++; } } return new int []{less + 1 , more - 1 }; }
BFPRT(面试聊) 俗称”中位数之中位数算法”。依靠一种精心设计的 pivot 选取方法,该算法从理论上保证了最坏情形下的线性时间复杂度,打败了平均线性、最坏 O(n^2) 复杂度的传统算法
bfprt算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public static int process (int [] arr, int L, int R, int index) { if (L == R){ return arr[L]; } int r = medianOfMedian(arr, L ,R); int [] range = partition(arr, L, R, r); if (index >= range[0 ] && index <= range[1 ]){ return arr[index]; } else if (index < range[0 ]){ return process(arr, L , range[0 ] - 1 , index); } else { return process(arr, range[1 ] + 1 , R, index); } } private static int medianOfMedian (int [] arr, int L, int R) { int size = R - L + 1 ; int offset = size % 5 == 0 ? 0 : 1 ; int [] m = new int [size/5 + offset]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m.length - 1 ; i++){ int first = L + i * 5 ; m[i] = sortAndMedian(arr, first, Math.min(R, first + 4 )); } return process(m, 0 , m.length - 1 , m.length / 2 ); } public static int sortAndMedian (int [] arr, int L, int R) { for (int i = L + 1 ; i <= R; i++) { for (int j = i - 1 ; j >= L && arr[j] > arr[j + 1 ]; j--) { swap(arr, j, j + 1 ); } } return arr[(L + R) / 2 ]; }
-堆排序- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 public static void heapSort (int [] arr) { if (arr.length < 2 || arr == null ) { return ; } int heapSize = arr.length; for (int i = arr.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { heapify(arr, i, arr.length); } swap(arr, 0 , --heapSize); while (heapSize > 0 ){ heapify(arr, 0 , heapSize); swap(arr, 0 , --heapSize); } } private static void heapify (int [] arr, int i, int heapSize) { int left = 2 * i + 1 ; while (left < heapSize){ int largest = left + 1 < heapSize && arr[left + 1 ] > arr[left] ? left + 1 : left; largest = arr[largest] > arr[i] ? largest : i; if (largest == i){ break ; } swap(arr, largest, i); i = largest; left = 432 * i + 1 ; } } private static void swap (int [] arr, int largest, int i) { int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[largest]; arr[largest] = temp; }
-归并排序- 1)整体是递归,左边排好序+右边排好序+merge让整体有序
递归版本 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public static void mergeSort1 (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } process(arr, 0 , arr.length - 1 ); } public static void process (int [] arr, int L, int R) { if (L == R) { return ; } int mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1 ); process(arr, L, mid); process(arr, mid + 1 , R); merge(arr, L, mid, R); } public static void merge (int [] arr, int L, int M, int R) { int [] help = new int [R - L + 1 ]; int i = 0 ; int p1 = L; int p2 = M + 1 ; while (p1 <= M && p2 <= R) { help[i++] = arr[p1] <= arr[p2] ? arr[p1++] : arr[p2++]; } while (p1 <= M) { help[i++] = arr[p1++]; } while (p2 <= R) { help[i++] = arr[p2++]; } for (i = 0 ; i < help.length; i++) { arr[L + i] = help[i]; } }
非递归版本 流程就在于折腾 步长 这个概念
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public static void mergeSort3 (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } int N = arr.length; int step = 1 ; while (step < N) { int L = 0 ; while (L < N) { int M = 0 ; if ( N - L >= step) { M = L + step - 1 ; } else { M = N - 1 ; } if (M == N -1 ) break ; int R = 0 ; if (N -1 - M >= step) { R = M + step; } else { R = N - 1 ; } merge(arr, L, M, R); if (R == N - 1 ) { break ; } else { L = R + 1 ; } } if (step > N / 2 ) { break ; } step <<= 1 ; } }
注意最后一组左组: L + step - 1 可能越界
从右往左合并就不用考虑越界问题了
1 2 3 if (step > N / 2) { break; }
此处不用等号的原因:
优化后的最终版本 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public static void mergeSort2 (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } int N = arr.length; int mergeSize = 1 ; while (mergeSize < N) { int L = 0 ; while (L < N) { int M = L + mergeSize - 1 ; if (M >= N) { break ; } int R = Math.min(M + mergeSize, N - 1 ); merge(arr, L, M, R); L = R + 1 ; } if (mergeSize > N / 2 ) { break ; } mergeSize <<= 1 ; } }
复杂度 一共执行次数 $log_2N$, merge 一次的复杂度 O(N)
-前缀树- 1)单个字符串中,字符从前到后的加到一棵多叉树上
可以完成前缀相关的查询
例子 设计一种结构。用户可以:
1 2 3 4 1)void insert(String str) 添加某个字符串,可以重复添加,每次算1个 2)int search(String str) 查询某个字符串在结构中还有几个 3) void delete(String str) 删掉某个字符串,可以重复删除,每次算1个 4)int prefixNumber(String str) 查询有多少个字符串,是以str做前缀的
前缀树的实现方式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 public static class Node { public int pass; public int end; public Node[] nexts; public Node () { pass = 0 ; end = 0 ; nexts = new Node [26 ]; } } public static class Trie1 { private Node root; public Trie1 () { root = new Node (); } public void insert (String word) { if (word == null ){ return ; } char [] str = word.toCharArray(); Node node = root; node.pass++; int path = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length; i++){ path = str[i] - 'a' ; if (node.nexts[path] == null ){ node.nexts[path] = new Node (); } node = node.nexts[path]; node.pass++; } node.end++; } public int search (String word) { if (word == null ){ return 0 ; } char [] str = word.toCharArray(); Node node = root; int path = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length; i++){ path = str[i] - 'a' ; if (node.nexts[path] == null ){ return 0 ; } node = node.nexts[path]; } return node.end; } public void delete (String word) { if (this .search(word) != 0 ){ char [] str = word.toCharArray(); Node node = root; node.pass--; int path = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length; i++){ path = str[i] - 'a' ; if (--node.nexts[path].pass == 0 ){ node.nexts[path] = null ; return ; } node = node.nexts[path]; } node.end--; } } public int prefixNode (String pre) { Node node = root; int path = 0 ; char [] str = pre.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length;i++){ path = str[i] - 'a' ; if (node.nexts[path] == null ){ return 0 ; } node = node.nexts[path]; } return node.pass; } }
-(桶排序)不基于比较的- 桶排序思想下的排序:计数排序 & 基数排序
1)桶排序思想下的排序都是不基于比较的排序
2)时间复杂度为O(N),额外空间负载度O(M)
3)应用范围有限,需要样本的数据状况满足桶的划分
计数排序和基数排序 计数排序要求,样本是整数,且范围比较窄
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public static void countSort (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { max = Math.max(max, arr[i]); } int [] bucket = new int [max + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { bucket[arr[i]]++; } int i = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < bucket.length; j++) { while (bucket[j]-- > 0 ) { arr[i++] = j; } } }
一般来讲,基数排序要求,样本是10进制的正整数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public static void radixSort (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } radixSort(arr, 0 , arr.length - 1 , maxbits(arr)); } public static int maxbits (int [] arr) { int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { max = Math.max(max, arr[i]); } int res = 0 ; while (max != 0 ) { res++; max /= 10 ; } return res; } public static void radixSort (int [] arr, int L, int R, int digit) { final int radix = 10 ; int i = 0 , j = 0 ; int [] help = new int [R - L + 1 ]; for (int d = 1 ; d <= digit; d++) { int [] count = new int [radix]; for (i = L; i <= R; i++) { j = getDigit(arr[i], d); count[j]++; } for (i = 1 ; i < radix; i++) { count[i] = count[i] + count[i - 1 ]; } for (i = R; i >= L; i--) { j = getDigit(arr[i], d); help[count[j] - 1 ] = arr[i]; count[j]--; } for (i = L, j = 0 ; i <= R; i++, j++) { arr[i] = help[j]; } } } public static int getDigit (int x, int d) { return ((x / ((int ) Math.pow(10 , d - 1 ))) % 10 ); }
1)一般来讲,计数排序要求,样本是整数,且范围比较窄
2)一般来讲,基数排序要求,样本是10进制的正整数
一旦要求稍有升级,改写代价增加是显而易见的
排序算法的稳定性 稳定性是指同样大小的样本再排序之后不会改变相对次序
对基础类型来说,稳定性毫无意义
对非基础类型来说,稳定性有重要意义
有些排序算法可以实现成稳定的,而有些排序算法无论如何都实现不成稳定的
排序算法总结
时间复杂度
额外空间复杂度
稳定性
选择排序
O(N^2)
O(1)
无
冒泡排序
O(N^2)
O(1)
有
插入排序
O(N^2)
O(1)
有
归并排序
O(N* logN)
O(N)
有
随机快排
O(N* logN)
O(logN)
无
堆排序
O(N* logN)
O(1)
无
计数排序
O(N)
O(M)
有
基数排序
O(N)
O(N)
有
1)不基于比较的排序,对样本数据有严格要求,不易改写
4 滑动窗口 滑动窗口更新结构
1 无重复数组的最长子串
给定一个字符串 找出里面没有重复的最长子串
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public static int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) { if (s.length() == 0 || s == "" ){ return 0 ; } HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet <Character>(); char [] str = s.toCharArray(); int ans = 0 ; int L = 0 ; int R = 0 ; while (L < str.length){ while (R < str.length && !set.contains(str[R])){ set.add(str[R]); R++; } ans = Math.max(ans, R - L ); set.remove(str[L]); L++; } return ans; }
动态规划版 使用256数组进行存储 先都初始化为-1 下标是字符串值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public static int lengthOfLongestSubstring2 (String s) { if (s.length() == 0 || s == "" ) { return 0 ; } char [] str = s.toCharArray(); int [] map = new int [256 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 256 ; i++) { map[i] = -1 ; } map[str[0 ]] = 0 ; int N = str.length; int ans = 1 ; int pre = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < N; i++) { pre = Math.min(i - map[str[i]], pre + 1 ); ans = Math.max(ans, pre); map[str[i]] = i; } return ans; }
2 最小覆盖子串
给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 "" 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public static String minLength2 (String s1, String s2) { if (s1 == null || s2 == null || s1.length() < s2.length()) { return "" ; } char [] str1 = s1.toCharArray(); char [] str2 = s2.toCharArray(); int [] map = new int [256 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i != str2.length; i++) { map[str2[i]]++; } int all = str2.length; int L = 0 ; int R = 0 ; int minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int start = 0 ; while (R != str1.length) { map[str1[R]]--; if (map[str1[R]] >= 0 ) { all--; } if (all == 0 ) { while (map[str1[L]] < 0 ) { map[str1[L]]++; L++; } if (minLen > R - L + 1 ){ minLen = R - L + 1 ; start = L; } all++; map[str1[L++]]++; } R++; } return minLen = = Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s1.substring(start, start + minLen); }
就是all还完之前r++往右展开 all==0 就要l++ 往左边缩
3 滑动窗口的最大值
假设一个固定大小为W的窗口;依次划过arr 返回每一次滑出状况的最大值
定义一个队列来作为窗口,里面放的是下标
循环遍历数组: L R边界
\1) 当窗口不为空&窗口结尾小于当前R 结尾弹出(window是单调递减)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 if ( arr == null || w < 1 || arr.length == 0 ){ return null ; } LinkedList<Integer> window = new LinkedList <>(); int [] res = new int [arr.length - w + 1 ]; for (int R = 0 ; R < arr.length; R++){ while (!window.isEmpty() && arr[window.peekLast()] < arr[R]){ window.pollLast(); } window.addLast(R); int L = R - w + 1 ; if (window.peekFirst() < L){ window.pollFirst(); } if (R >= w - 1 ){ res[L] = arr[window.peekFirst()]; } } return res;
4 满足绝对值差达标的子数组数量
给定一个整型数组arr, 和一个整数num 某一个arr中的子数组sub 如果想达标必须满足 sub中最大值 - sub中国最小值 <= num 返回arr中达标子数组的数量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 public class SW_AllLessNumSubArray { public static int allLessNumSubArray (int [] arr, int num) { if (arr.length == 0 || arr == null ) { return 0 ; } LinkedList<Integer> qmin = new LinkedList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> qmax = new LinkedList <>(); int L = 0 ; int R = 0 ; int res = 0 ; while (L < arr.length) { while (R < arr.length) { while (!qmax.isEmpty() && arr[qmax.peekLast()] <= arr[R]) { qmax.pollLast(); } qmax.addLast(R); while (!qmin.isEmpty() && arr[qmin.peekLast()] >= arr[R]) { qmin.pollLast(); } qmin.addLast(R); if (arr[qmax.getFirst()] - arr[qmin.getFirst()] > num) { break ; } R++; } res += R - L; if (qmax.peekFirst() == L) { qmax.pollFirst(); } if (qmin.peekFirst() == L) { qmin.pollFirst(); } L++; } return res; } }
5 二叉树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class TreeNode { private int val; private TreeNode left; private TreeNode right; public TreeNode (int val, int left, int right) { this .val = val; this .left = left; this .right = right; } }
1 二叉树先、中、后序遍历(DFS) 递归 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void process (TreeNode head) { process(head.left); process(head.right); }
非递归(压栈)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public void front (TreeNode head) { if (head == null ) { return ; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(head); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode cur = stack.pop(); sysout(); if (cur.right != null ) { stack.push(cur.right); } if (cur.left != null ) { stack.push(cur.left); } } return ; }
后:用两个栈 1)先压左再压右 同时答应弹出改为压入另一个栈 输出—》 头右左 2)最后输出的时候就是左右头 头左右
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public void process (TreeNode head) { if (head == null ) {return ;} Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack <>(); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode cur = stack.pop(); stack2.push(cur.val); if (cur.left != null ) { stack.push(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ) { stack.push(cur.right); } } while (!stack2.isEmpty()) { TreeNode cur = stack.pop(); sysout(); } return ; }
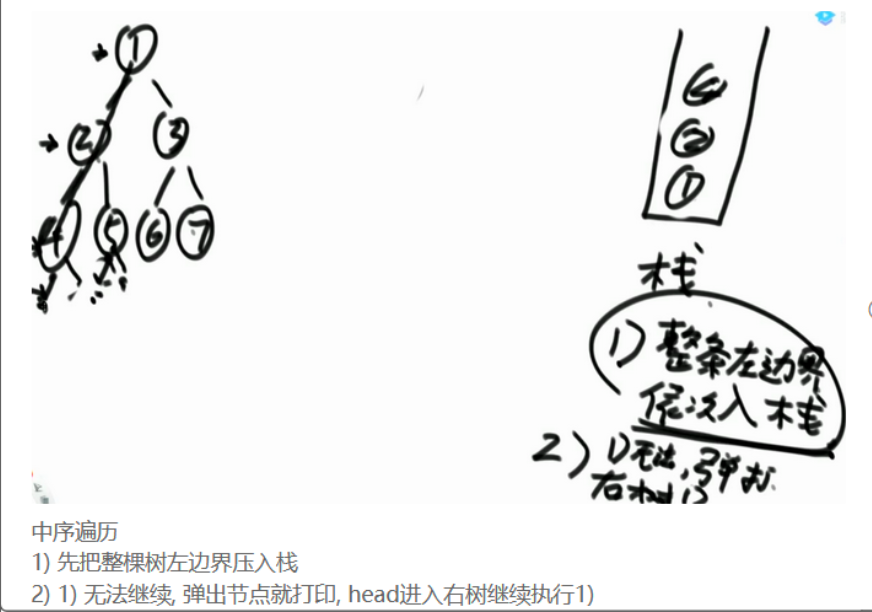
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public void process (TreeNode head) { if (head != null ) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null ) { if (head != null ) { stack.push(head); head = head.left; } else { head = stack.pop(); sysout(head.val); head = head.right; } } } return ; }
二叉搜索树也可以用这个
2 二叉树的层序遍历(BFS) 给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)
1) 打印每一层
给你二叉树的根节点root, 返回其节点值的层序遍历,就是逐层打印
1.先定义结果集res 和判空操作
2.定义队列容器 ,head放入队列中。
3.定义结果集元素list 即每一层。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public static List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode head) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (head == null ) { return res; } Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList <>(); q.add(head); while (!q.isEmpty()) { int size = q.size(); List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { TreeNode cur = q.poll(); list.add(cur.val); if (cur.left != null ) { q.add(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ) { q.add(cur.right); } } res.add(list); } return res; }
二叉树的锯齿形遍历
就是在层序遍历基础上 使用flag来判断打印的顺序 ⚠️list.add(0, root.val) 就是添加到开头
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder (TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <List<Integer>>(); if (root == null ){ return res; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <TreeNode>(); queue.add(root); boolean flag = true ; while (! queue.isEmpty()){ List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <Integer>(); int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; ++i){ root = queue.poll(); if (flag){ list.add(root.val); }else { list.add(0 , root.val); } if (root.left != null ){ queue.add(root.left); } if (root.right != null ){ queue.add(root.right); } } flag = !flag; res.add(list); } return res; }
2)返回节点最多的那一层
需要curEnd记录是否当前到层的结尾 需要nextEnd记录下一层的最后节点
将上面层序遍历添加每层元素的过程改为记录层的curSize
当cur == curEnd 时 更新 ans (maxWidth
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public static int maxWidth (TreeNode head) { int ans = 0 ; if (head == null ) { return ans; } int curSize = 0 ; }
3)二叉树的右视图
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
需要curEnd记录是否当前到层的结尾 需要nextEnd记录下一层的最后节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (head == null ) { return res; } TreeNode curEnd = head; TreeNode nextEnd = null ; Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList <>(); q.add(head); while (!q.isEmpty()) { TreeNode cur = q.poll(); if (cur.left != null ) { q.add(cur.left); nextEnd = cur.left; } if (cur.right != null ) { q.add(cur.right); nextEnd = cur.right; } if (cur == curEnd) { res.add(cur.val); curEnd = nextEnd; } } return res;
4)最大宽度(左右节点的距离)
给定一个二叉树,编写一个函数来获取这个树的最大宽度。树的宽度是所有层中的最大宽度。这个二叉树与满二叉树(full binary tree)结构相同,但一些节点为空。
每一层的宽度被定义为两个端点(该层最左和最右的非空节点,两端点间的null节点也计入长度)之间的长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 避免不了要记录每一个节点的index 所以需要一个新的节点结构 newnode{ treenode node; int level; int pos; }
在层序遍历基础上 队列添加的是一个新的节点结构来对每个节点的层数和position进行记录 不需要
每次队列进行一次poll循环都要检查 如果curlever != cur.level 说明到了下一层,将curlevel更新,用first抓住第一个的pos
更新max
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public int widthOfBinaryTree (TreeNode root) { Queue<NewNode> q = new LinkedList <>(); q.add(new NewNode (root, 0 , 0 )); int ans = 0 ; int curlevel = 0 ; int firstpos = 0 ; while (!q.isEmpty()){ NewNode cur = q.poll(); if (cur.node.left != null ){ q.add(new NewNode (cur.node.left, cur.level + 1 , cur.pos * 2 )); } if (cur.node.right != null ){ q.add(new NewNode (cur.node.right, cur.level + 1 , cur.pos * 2 + 1 )); } if (curlevel != cur.level){ curlevel = cur.level; firstpos = cur.pos; } ans = Math.max(ans, cur.pos - firstpos + 1 ); } return ans; } public class NewNode { private TreeNode node; private int level; private int pos; public NewNode (TreeNode node, int level, int pos) { this .node = node; this .level = level; this .pos = pos; } }
3 二叉树的最近公共祖先
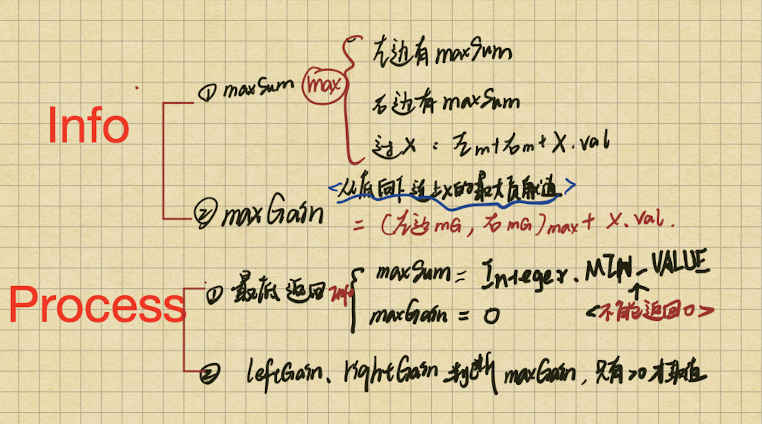
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
Info{boolean findP, boolean findQ, treenode ans}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { return process(root,p,q).ans; } public static class Info { public boolean findP; public boolean findQ; public TreeNode ans; public Info (boolean findP, boolean findQ, TreeNode ans) { this .findP = findP; this .findQ = findQ; this .ans = ans; } } private Info process (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == null ){ return new Info (false , false , null ); } Info leftInfo = process(root.left, p, q); Info rightInfo = process(root.right, p, q); boolean findP = leftInfo.findP || rightInfo.findP || (root == p); boolean findQ = leftInfo.findQ || rightInfo.findQ || (root == q); TreeNode ans = null ; if (leftInfo.ans != null ){ ans = leftInfo.ans; }else if (rightInfo.ans != null ){ ans = rightInfo.ans; }else if (findP && findQ){ ans = root; } return new Info (findP, findQ, ans); }
4 二叉树最大路径和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public int maxPathSum (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } return process(root).maxSum; } public static class Info { public int maxGain; public int maxSum ; public Info (int m1, int m2) { maxGain = m1; maxSum = m2; } } public static Info process (TreeNode head) { if (head == null ){ return new Info (0 , Integer.MIN_VALUE); } Info leftInfo = process(head.left); Info rightInfo = process(head.right); int leftGain = Math.max(leftInfo.maxGain, 0 ); int rightGain = Math.max(rightInfo.maxGain, 0 ); int maxGain = Math.max(leftGain,rightGain) + head.val; int maxSum = Math.max( Math.max(leftInfo.maxSum,rightInfo.maxSum), leftGain + rightGain + head.val); return new Info (maxGain, maxSum); }
5 对称二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { return isMirror(root, root); } public static boolean isMirror (TreeNode h1, TreeNode h2) { if (h1 == null && h2 == null ){ return true ; } if (h1 != null && h2 != null ){ return (h1.val == h2.val) && isMirror(h1.left, h2.right) && isMirror(h1.right, h2.left); } return false ; }
6 从前序和中序序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public TreeNode buildTree (int [] pre, int [] in) { if (pre == null || in == null || pre.length != in.length){ return null ; } return f(pre, 0 , pre.length- 1 , in, 0 , in.length - 1 ); } private TreeNode f (int [] pre, int L1, int R1, int [] in, int L2, int R2) { if (L1 > R1){ return null ; } TreeNode head = new TreeNode (pre[L1]); if (L1 == R1){ return head; } int find = L2; while (in[find] != pre[L1]){ find++; } head.left = f(pre, L1 + 1 , L1 + (find - L2), in, L2, find - 1 ); head.right = f(pre, L1 + (find - L2) + 1 , R1, in, find + 1 , R2); return head; } }
7 验证二叉搜索树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public static boolean isValidBST (TreeNode head) { if (head != null ){ Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <TreeNode>(); double last = -Double.MAX_VALUE; while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null ){ if (head != null ){ stack.push(head); head = head.left; }else { head = stack.pop(); if (head.val <= last){ return false ; } last = head.val; head = head.right; } } } return true ; }
8 平衡二叉树 使用递归套路
1 2 3 4 INFO { 高度; 是否是平衡二叉树; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) { return process(root).isBt; } public static class Info { private int height; private boolean isBt; public Info (int h, boolean ib) { height = h; isBt = ib; } } public static Info process (TreeNode head) { if (head == null ){ return new Info (0 , true ); } Info leftInfo = process(head.left); Info rightInfo = process(head.right); int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1 ; boolean isBalanced = false ; if (leftInfo.isBt && rightInfo.isBt && Math.abs(leftInfo.height - rightInfo.height) <= 1 ){ isBalanced = true ; } return new Info (height, isBalanced); }
9 二叉树的序列化和反序列化
思路
序列化: 准备一个string的队列 然后按照先序顺序将结点转为String类型然后加入队列,左边和右边结点按照顺序递归执行该方法
反序列化: 将要转化为二叉树的队列传入,然后弹出结点为head(注意转换回为Int类型),head左边递归执行preb(prelist),右边递归执行preb(prelist)
错误
判断null值注意判断哈 特别是递归里面 就算是方法前面判断了 当时不代表递归以后不会再次出现,所以方法内还要再判断一次
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public class BT_09_preSerial { public static Queue<String> preSerial (TreeNode head) { Queue<String> ans = new LinkedList <>(); pre(head, ans); return ans; } private static void pre (TreeNode head, Queue<String> ans) { if (head == null ){ ans.add(null ); }else { ans.add(String.valueOf(head.val)); pre(head.left, ans); pre(head.right, ans); } } public static TreeNode buildByPreQueue (Queue<String> prelist) { if (prelist == null || prelist.size() == 0 ){ return null ; } return preb(prelist); } private static TreeNode preb (Queue<String> prelist) { String value = prelist.poll(); if (value == null ){ return null ; } TreeNode head = new TreeNode (Integer.valueOf(value)); head.left = preb(prelist); head.right = preb(prelist); return head; } }
10 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
3
/
返回它的最大深度 3 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { return findDepth(root).height; } public static class Info { public int height; public Info (int h) { height = h; } } public static Info findDepth (TreeNode head) { if (head == null ){ return new Info (0 ); } Info leftInfo = findDepth(head.left); Info rightInfo = findDepth(head.right); int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1 ; return new Info (height); } }
11 最大直径
给定一棵二叉树,你需要计算它的直径长度。一棵二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。
示例 :
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
返回 3, 它的长度是路径 [4,2,1,3] 或者 [5,2,1,3]。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public class BT_05_ZhiJing { static int ans = 1 ; public int max (TreeNode head) { return process(head) - 1 ; } public static int process (TreeNode head) { if (head == null ){ return 0 ; } int lM = process(head.left); int rM = process(head.right); ans = Math.max(lM + rM + 1 , ans); return Math.max(lM, rM) + 1 ; } public int max2 (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } return process2(root).max; } public static class Info { public Integer height; public Integer max; public Info (Integer h, Integer m) { height = h; max = m; } } private Info process2 (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return new Info (0 , 0 ); } Info leftInfo = process2(root.left); Info rightInfo = process2(root.right); int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1 ; int max = Math.max(Math.max(leftInfo.max, rightInfo.max), leftInfo.height + rightInfo.height); return new Info (height, max); } }
12 路径总和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 public static boolean isSum; public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if (root == null ) { return false ; } isSum = false ; process(root, 0 , targetSum); return isSum; } public void process (TreeNode head, int preSum, int sum) { if (head.left == null && head.right == null ) { if (preSum + head.val == sum) { isSum = true ; } return ; } preSum += head.val; if (head.left != null ) { process(head.left, preSum, sum); } if (head.right != null ) { process(head.right, preSum, sum); } } public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) { return ans; } List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>(); process(root, path, 0 , targetSum, ans); return ans; } public void process (TreeNode head, List<Integer> path, int preSum, int sum, List<List<Integer>> ans) { if (head.left == null && head.right == null ) { if (head.val + preSum == sum) { path.add(head.val); ans.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } } preSum += head.val; path.add(head.val); if (head.left != null ) { process(head.left, path, preSum, sum, ans); } if (head.right != null ) { process(head.right, path, preSum, sum, ans); } path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); }
13 翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 翻转二叉树 public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return null ; } TreeNode left = root.left; root.left = invertTree(root.right); root.right = invertTree(left); return root; }
6 栈 1 有效括号
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
遍历所有左边的括号变成对应的右括号压入栈
遇到的右边的括号
如果stack是空的,则false
弹出栈顶比较不相等 false
最后stack 必须是空的才能满足
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public boolean isValid (String s) { char [] str = s.toCharArray(); Stack<Character> stack = new Stack <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length; i++) { if (str[i] == '(' || str[i] == '[' || str[i] == '{' ) { stack.push(str[i]); } else { if (stack.isEmpty()) { return false ; } char cur = stack.pop(); if ((str[i] == ')' && cur != '(' ) || (str[i] == '}' && cur != '{' ) || (str[i] == ']' && cur != '[' )) { return false ; } } } return stack.isEmpty(); }
2 用栈实现队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class MyQueue { private Stack<Integer> sPop; private Stack<Integer> sPush; public MyQueue () { sPop = new Stack <Integer>(); sPush = new Stack <Integer>(); } public void push (int x) { sPush.push(x); } public int pop () { if (sPop.isEmpty()){ while (!sPush.isEmpty()){ sPop.push(sPush.pop()); } } return sPop.pop(); } public int peek () { if (sPop.isEmpty()){ while (!sPush.isEmpty()){ sPop.push(sPush.pop()); } } return sPop.peek(); } public boolean empty () { if (sPop.isEmpty() && sPush.isEmpty()){ return true ; } else { return false ; } } }
3 最小栈
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
push(x) —— 将元素 x 推入栈中。pop() —— 删除栈顶的元素。top() —— 获取栈顶元素。getMin() —— 检索栈中的最小元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class MinStack { public Stack<Integer> data; public Stack<Integer> min; public MinStack () { this .data = new Stack <Integer>(); this .min = new Stack <Integer>(); } public void push (int val) { if (this .min.isEmpty()){ this .min.push(val); }else if (val < this .getMin()){ this .min.push(val); }else { this .min.push(this .getMin()); } this .data.push(val); } public void pop () { this .data.pop(); this .min.pop(); } public int top () { return this .data.peek(); } public int getMin () { return this .min.peek(); } }
4 两个队列实现栈 在push操作里进行改进就可以:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class MyStack { public Queue<Integer> q1; public Queue<Integer> q2; public MyStack () { q1 = new LinkedList <Integer>(); q2 = new LinkedList <Integer>(); } public void push (int x) { q2.offer(x); while (!q1.isEmpty()){ q2.offer(q1.poll()); } Queue<Integer> tmp = q1; q1 = q2; q2 = tmp; } public int pop () { return q1.poll(); } public int top () { return q1.peek(); } public boolean empty () { return q1.isEmpty(); } }
用一个队列也可以
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void push (int x) { int n = queue.size(); queue.offer(x); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { queue.offer(queue.poll()); } }
5 单调栈 为了解决给定的一个可能含有重复值的arr,i位置一定有以下信息
1)arr[i] 左边有离它最近比它小的(大)的数
2)arr[i] 右边有离它最近比它小的(大)的数
找到左边和右边离i最近比其小的下表对 res[n][2] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 public class Code1_MonotonousStack { public static int [][] getNearLessNoRepeat(int [] arr){ int [][] res = new int [arr.length][2 ]; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++){ while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek()] > arr[i]){ int popIndex = stack.pop(); int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek(); res[popIndex][0 ] = leftLessIndex; res[popIndex][1 ] = i; } stack.push(i); } while (!stack.isEmpty()){ int popIndex = stack.pop(); int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek(); res[popIndex][0 ] = leftLessIndex; res[popIndex][1 ] = -1 ; } return res; } public static int [][] getNearLess(int [] arr){ int [][] res = new int [arr.length][2 ]; Stack<List<Integer>> stack = new Stack <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++){ while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek().get(0 )] > arr[i]){ List<Integer> popIndex = stack.pop(); int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek().get(stack.peek().size() - 1 ); for (Integer popi : popIndex){ res[popi][0 ] = leftLessIndex; res[popi][1 ] = i; } } if (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek().get(0 )] == arr[i]){ stack.peek().add(Integer.valueOf(i)); }else { List<Integer> pushIndex = new ArrayList <>(); pushIndex.add(Integer.valueOf(i)); stack.push(pushIndex); } } while (!stack.isEmpty()){ List<Integer> popIndex = stack.pop(); int leftLessIndex = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek().get(stack.peek().size() - 1 ); for (Integer popi : popIndex){ res[popi][0 ] = leftLessIndex; res[popi][1 ] = -1 ; } } return res; } }
正数数组arr中(sub的累加和*min)的最大值
给定一个只包含正数的数组arr,arr中任何一个子数组sub,一定都可以算出(sub累加和 )* (sub中的最小值)是什么,
直接找每个数两边最近比它小中间部分累加和(这部分该数一定最小)
1 建立前缀和数组sums[i](这样求累加和就可以[0R] -[0L-1])
2 和上面单调栈思路差不多
1)栈顶弹出[j]后更新max
2)再遍历栈里的元素 右边没有比它最小所以累加直接用sums[N-1]来减
7 递归 1 全排列
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public static List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <Integer>(); if (nums.length == 0 || nums == null ){ return ans; } for (int num : nums) { path.add(num); } process(path, 0 , ans); return ans; } public static void process (List<Integer> path, int i, List<List<Integer>> ans) { if (i == path.size()){ ans.add(new ArrayList <Integer>(path)); } boolean [] vis = new boolean [256 ]; for (int j = i; j < path.size(); j++){ if (!vis[path.get(j) + 128 ]){ vis[path.get(j) + 128 ] = true ; Collections.swap(path, i, j); process(path, i + 1 , ans); Collections.swap(path, i, j); } } }
全排列2⃣️ 不重复 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public class Recursion 回溯_Permutation { public static List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>(); for (int num : nums){ path.add(num); } process(path, 0 , ans); return ans; } public static void process (List<Integer> path, int i, List<List<Integer>> ans) { if (i == path.size()){ ans.add(new ArrayList <Integer>(path)); } boolean [] vis = new boolean [256 ]; for (int j = i; j < path.size(); j++){ if (!vis[path.get(j)]+128 ){ vis[path.get(j)+128 ] = true ; Collections.swap(path, i, j); process(path, i + 1 , ans); Collections.swap(path, i, j); } } } }
2 括号生成
数字 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你设计一个函数,用于能够生成所有可能的并且 有效的 括号组合。
1 2 3 4 利用一个原理是 当前面已经做了选择的左括号比右括号多的时候 就添加右括号 需要剪枝 在往path里面添加括号的时候 进行条件剪枝
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public List<String> generateParenthesis (int n) { char [] path = new char [n << 1 ]; List<String> ans = new ArrayList <>(); process(path,0 , n, 0 , ans); return ans; } public static void process (char [] path, int i,int leftRest, int leftMinusRight, List<String> ans ) { if (i == path.length){ ans.add(String.valueOf(path)); } else { if (leftRest > 0 ){ path[i] = '(' ; process(path, i + 1 , leftRest - 1 , leftMinusRight + 1 , ans); } if (leftMinusRight > 0 ){ path[i] = ')' ; process(path, i + 1 , leftRest, leftMinusRight - 1 , ans); } } }
3 复原ip地址
有效 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 ‘.’ 分隔。
例如:”0.1.2.201” 和 “192.168.1.1” 是 有效 IP 地址,但是 “0.011.255.245”、”192.168.1.312” 和 “192.168@1.1 “ 是 无效 IP 地址。
给定一个只包含数字的字符串 s ,用以表示一个 IP 地址,返回所有可能的有效 IP 地址,这些地址可以通过在 s 中插入 ‘.’ 来形成。你 不能 重新排序或删除 s 中的任何数字。你可以按 任何 顺序返回答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 static final int COUNT = 4 ; int [] segment; List<String> ans = new ArrayList <>(); public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) { segment = new int [COUNT]; dfs(s, 0 , 0 ); return ans; } public void dfs (String s, int id, int segStart) { if (id == COUNT) { if (segStart == s.length()) { StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer (); for (int i = 0 ; i < COUNT; i++) { str.append(segment[i]); if (i != COUNT - 1 ) { str.append('.' ); } } ans.add(str.toString()); } return ; } if (segStart == s.length()) { return ; } if (s.charAt(segStart) == '0' ) { segment[id] = 0 ; dfs(s, id + 1 , segStart + 1 ); } int ans = 0 ; for (int segEnd = segStart; segEnd < s.length(); segEnd++) { ans = ans * 10 + (s.charAt(segEnd) - '0' ); if (ans > 0 && ans <= 0xFF ) { segment[id] = ans; dfs(s, id + 1 , segEnd + 1 ); } else { break ; } } }
4 单词搜索 dfs+回溯
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution { public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { int h = board.length, w = board[0 ].length; boolean [][] visited = new boolean [h][w]; for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { boolean flag = check(board, visited, i, j, word, 0 ); if (flag) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public boolean check (char [][] board, boolean [][] visited, int i, int j, String s, int k) { if (board[i][j] != s.charAt(k)) { return false ; } else if (k == s.length() - 1 ) { return true ; } visited[i][j] = true ; int [][] directions = {{0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 }}; boolean result = false ; for (int [] dir : directions) { int newi = i + dir[0 ], newj = j + dir[1 ]; if (newi >= 0 && newi < board.length && newj >= 0 && newj < board[0 ].length) { if (!visited[newi][newj]) { boolean flag = check(board, visited, newi, newj, s, k + 1 ); if (flag) { result = true ; break ; } } } } visited[i][j] = false ; return result; } }
5 子集
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public static List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>(); if (nums.length == 0 || nums == null ){ return res; } process2(nums, 0 , res, path); return res; } private static void process2 (int [] nums, int i, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path) { if (i == nums.length){ res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } process2(nums, i + 1 , res, path); List<Integer> path2 = new ArrayList <>(path); path2.add(nums[i]); process2(nums, i + 1 , res, path2); }
8 并查集 并查集 用来解决图的连通性和环的数量
结构(hash表) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 public class Code01_UnionFind { public static class Node <V> { V value; public Node (V v) { value = v; } } public static class UnionFind <V> { public HashMap<V, Node<V>> nodes; public HashMap<Node<V>, Node<V>> parents; public HashMap<Node<V>, Integer> sizeMap; public UnionFind (List<V> values) { nodes = new HashMap <>(); parents = new HashMap <>(); sizeMap = new HashMap <>(); for (V cur : values) { Node<V> node = new Node <>(cur); nodes.put(cur, node); parents.put(node, node); sizeMap.put(node, 1 ); } } public Node<V> findFather (Node<V> cur) { Stack<Node<V>> path = new Stack <>(); while (cur != parents.get(cur)) { path.push(cur); cur = parents.get(cur); } while (!path.isEmpty()) { parents.put(path.pop(), cur); } return cur; } public boolean isSameSet (V a, V b) { return findFather(nodes.get(a)) == findFather(nodes.get(b)); } public void union (V a, V b) { Node<V> aHead = findFather(nodes.get(a)); Node<V> bHead = findFather(nodes.get(b)); if (aHead != bHead) { int aSize = sizeMap.get(aHead); int bSize = sizeMap.get(bHead); Node<V> small = aSize < bSize ? aHead : bHead; Node<V> big = small == aHead ? bHead : aHead; parents.put(small, big); sizeMap.put(big, aSize + bSize); sizeMap.remove(small); } } public int sets () { return sizeMap.size(); } } }
1 岛屿数量
给你一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public static int numIslands (char [][] board) { int islands = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < board.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < board[0 ].length; j++) { if (board[i][j] == '1' ) { islands++; infect(board, i, j); } } } return islands; } public static void infect (char [][] board, int a, int b) { if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= board.length || j >= board[0 ].length || board[i][j] != '1' ) { return ; } board[i][j] = 0 ; infect1(board, i, j - 1 ); infect1(board, i, j + 1 ); infect1(board, i + 1 , j); infect1(board, i - 1 , j); } } public static void infect2 (char [][] board, int a, int b) { Queue<int []> list = new LinkedList <>(); list.add(new int [] { a, b }); while (!list.isEmpty()) { int [] cur = list.poll(); int i = cur[0 ]; int j = cur[1 ]; if (i >= 0 && j >= 0 && i < board.length && j < board[0 ].length && board[i][j] == '1' ) { board[i][j] = 0 ; list.add(new int [] { i - 1 , j }); list.add(new int [] { i + 1 , j }); list.add(new int [] { i, j - 1 }); list.add(new int [] { i, j + 1 }); } }
使用并查集(面试) 为什么要并查集? 如果有多台cpu 大岛变成小岛就会很容易
面试就讲一下怎么通过并查集来进行union : 并查集就是可以将a, b所在的集合进行合并;需要每个岛的位置 所以需要一个index方法来返回每格子的位置就是行数乘以矩阵宽度再加上列数, 然后要进行union() 具体过程就是先找到两个要合并的点的父亲,如果不相同就再调出两个所在集合的大小sizemap,然后将小的集合接在大的集合下面, 更新sizemap。 这里找父亲的操作可以用一个help数组倒序遍历来代替栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 public static int numIslands2 (char [][] board) { int row = board.length; int col = board[0 ].length; UnionFind2 uf = new UnionFind2 (board); for (int j = 1 ; j < col; j++) { if (board[0 ][j - 1 ] == '1' && board[0 ][j] == '1' ) { uf.union(0 , j - 1 , 0 , j); } } for (int i = 1 ; i < row; i++) { if (board[i - 1 ][0 ] == '1' && board[i][0 ] == '1' ) { uf.union(i - 1 , 0 , i, 0 ); } } for (int i = 1 ; i < row; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < col; j++) { if (board[i][j] == '1' ) if (board[i][j - 1 ] == '1' ) { uf.union(i, j - 1 , i, j); } if (board[i - 1 ][j] == '1' ) { uf.union(i - 1 , j, i, j); } } } } return uf.sets(); } public static class UnionFind2 { private int [] parent; private int [] size; private int [] help; private int col; private int sets; public UnionFind2 (char [][] board) { col = board[0 ].length; sets = 0 ; int row = board.length; int len = row * col; parent = new int [len]; size = new int [len]; help = new int [len]; for (int r = 0 ; r < row; r++) { for (int c = 0 ; c < col; c++) { if (board[r][c] == '1' ) { int i = index(r, c); parent[i] = i; size[i] = 1 ; sets++; } } } } private int index (int r, int c) { return r * col + c; } private int find (int i) { int hi = 0 ; while (i != parent[i]) { help[hi++] = i; i = parent[i]; } for (hi--; hi >= 0 ; hi--) { parent[help[hi]] = i; } return i; } public void union (int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2) { int i1 = index(r1, c1); int i2 = index(r2, c2); int f1 = find(i1); int f2 = find(i2); if (f1 != f2) { if (size[f1] >= size[f2]) { size[f1] += size[f2]; parent[f2] = f1; } else { size[f2] += size[f1]; parent[f1] = f2; } sets--; } } public int sets () { return sets; } }
2 省份数量(朋友圈)
有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 public int findCircleNum (int [][] M) { int N = M.length; UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind (N); for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { for (int j = i+1 ; j < N; j++) { if (M[i][j] == 1 ) { unionFind.union(i, j); } } } return unionFind.sets(); } public static class UnionFind { private int [] parents; private int [] size; private int [] help; private int sets; public UnionFind (int N) { parents = new int [N]; size = new int [N]; help = new int [N]; sets = N; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { parents[i] = i; size[i] = 1 ; } } public int findFather (int i) { int hi = 0 ; while ( i != parents[i]) { help[hi++] = i; i = parents[i]; } for (hi--; hi >=0 ; hi--){ parents[help[hi]] = i; } return i; } public void union (int i, int j) { int iF = findFather(i); int jF = findFather(j); if (iF != jF) { if (size[iF] < size[jF]) { size[jF] += size[iF]; parents[iF] = jF; }else { size[iF] += size[jF]; parents[jF] = iF; } sets--; } } public int sets () { return sets; } }
7 图 将矩阵转化为自己的结构(creatGraph)
new一个自己的graph
遍历矩阵每一行 for(matrix.length)
weight:matrix[i][0] from[i][1] to:[i][2]
判断是否contanskey(from和to) 分别放入点集
edge初始化 并赋值 (weight,fromNode,toNode)
更新出入度、直接点、直接边
边放入边集
1 图的bfs 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Code01_BFS { public static void bfs (Node start) { if (start == null ) { return ; } Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList <>(); HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet <>(); queue.add(start); set.add(start); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node cur = queue.poll(); System.out.println(cur.value); for (Node next : cur.nexts) { if (!set.contains(next)) { set.add(next); queue.add(next); } } } } }
2 DFS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 package all.Graph;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Stack;public class Code02_DFS { public static void dfs (Node node) { if (node == null ) { return ; } Stack<Node> stack = new Stack <>(); HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet <>(); stack.add(node); set.add(node); System.out.println(node.value); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Node cur = stack.pop(); for (Node next : cur.nexts) { if (!set.contains(next)) { stack.push(cur); stack.push(next); set.add(next); System.out.println(next.value); break ; } } } } }
3 拓扑排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class Code03_TopologySort { public static List<Node> sortedTopology (Graph graph) { HashMap<Node, Integer> inMap = new HashMap <>(); Queue<Node> zeroInQueue = new LinkedList <>(); for (Node node : graph.nodes.values()) { inMap.put(node, node.in); if (node.in == 0 ) { zeroInQueue.add(node); } } List<Node> result = new ArrayList <>(); while (!zeroInQueue.isEmpty()) { Node cur = zeroInQueue.poll(); result.add(cur); for (Node next : cur.nexts) { inMap.put(next, inMap.get(next) - 1 ); if (inMap.get(next) == 0 ) { zeroInQueue.add(next); } } } return result; } }